In a nutshell
Despite some recovery in levels of economic activity and employment, households and firms in the Middle East and North Africa were still experiencing steep income and revenue losses well into the pandemic’s second year.
Social support reached a relatively limited fraction of the population, except in Jordan. Assistance was generally well targeted, reaching lower-income households more often than higher-income households.
The reach of policies supporting firms was also limited with up to three-quarters of small and medium enterprises reporting they had not applied for or received any government assistance; firms in Jordan and Morocco were experiencing more difficulty than firms in Egypt and Tunisia in the first quarter of 2021.
With the Covid-19 pandemic on the verge of its third year, Middle East and North African (MENA) economies are recovering from the slump caused by lockdowns and other economic disruptions, but households and firms are still experiencing steep income and revenue losses well into the pandemic’s second year.
In two recently published policy briefs, we examine how workers and firms have fared in the first half of 2021 in Egypt, Jordan, Morocco and Tunisia (Krafft et al, 2021, 2022).
Household and enterprise surveys during the pandemic
The analysis is based on the COVID-19 MENA Monitor Household and Enterprise Surveys conducted by ERF over the second half of 2020 and the first half of 2021 (OAMDI – Open Access Micro Data Initiative, 2021a, 2021b).
The surveys were conducted by telephone on a panel of firms and enterprises. The household surveys are the main source of information on how households, workers and microenterprises experienced the pandemic, whereas the enterprise surveys focused on the experience of small and medium enterprises (those with between six and 199 workers) in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Four waves of the household survey were conducted in Morocco and Tunisia centred around November 2020, February 2021, April 2021 and June 2021. Two waves were conducted in Egypt and Jordan centred around February and June 2021.
Two waves of the enterprise surveys were conducted in each of the four countries corresponding to the first and second quarter of 2021. Household and enterprise surveys were conducted in Sudan as part of the same series, but are not discussed here.
Health and economic outcomes in the pandemic
Among the four countries, Jordan and Tunisia experienced much higher rates of Covid-19 cases and deaths in the first half of 2021 than either Egypt or Morocco. But while Egypt gradually loosened its closure measures in 2021, Morocco, like Jordan and Tunisia, maintained more stringent measures than the world average.
Egypt was also the only one among the four countries that managed to maintain a positive economic growth rate of 1.5% in 2020. In contrast, Tunisia experienced a large economic contraction of 8.8% and Morocco likewise contracted 6.3%, while Jordan’s economy contracted by 1.6%. Despite relatively strong recoveries in Morocco and Tunisia in the first half of 2021, their economies, as well as that of Jordan, remained depressed relative to pre-pandemic levels.
The tourist and transport industries were the hardest hit in all four countries, with tourism-related industries the most negatively affected in terms of closures, reduced hours and revenue losses.
Labour market outcomes
The evidence suggests that aggregate labour market indicators, such as labour force participation, employment and unemployment rates, were recovering in the first half of 2021, except in Morocco where the progress made earlier in the year later reversed. With the exception of Morocco, more of those who lost jobs early in the pandemic were regaining employment over the course of 2021.
Private wage workers, especially those hired informally, faced substantially more challenges related to layoffs/suspensions and wage reductions in Egypt, Jordan and Tunisia than in Morocco. But the prevalence of these challenges decreased in these three countries from February to June 2021, while it increased in Morocco.
The results of the household and enterprise surveys suggest that microenterprises were the most likely to be closed due to Covid-19 in the first quarter of 2021. If open, micro and small firms were more likely to have reduced hours than medium firms.
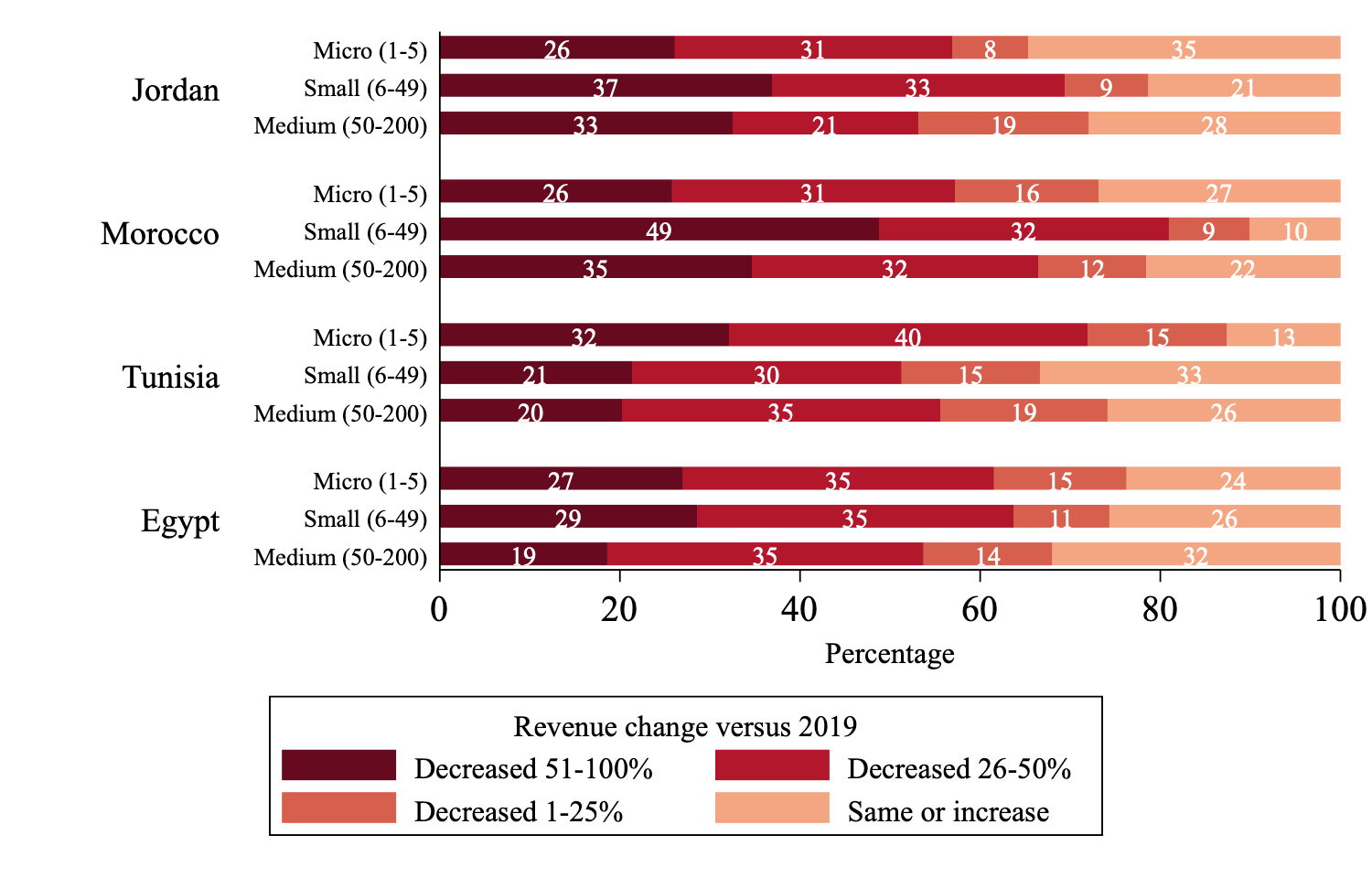
As Figure 1 shows, a similar proportion of microenterprises across the four countries reported substantially reduced revenues, but higher proportions of small and medium enterprises reported such revenue losses in Jordan and Morocco than in Egypt and Tunisia in the first quarter of 2021.
Figure 1: Revenue change (past 60 days versus 2019), by firm size in February 2020 and country, micro, small and medium enterprises (percentage), quarter one, 2021.
Source: Krafft et al (2021), based on data from the ERF COVID-19 MENA Monitor Household and Enterprise Surveys
Income levels
Despite some recovery in employment rates, household income levels remain depressed, with just under a half to two-thirds of households in all four countries reporting income losses in June 2021 compared to pre-pandemic levels. In fact, the share reporting income losses increased from February to June 2021.
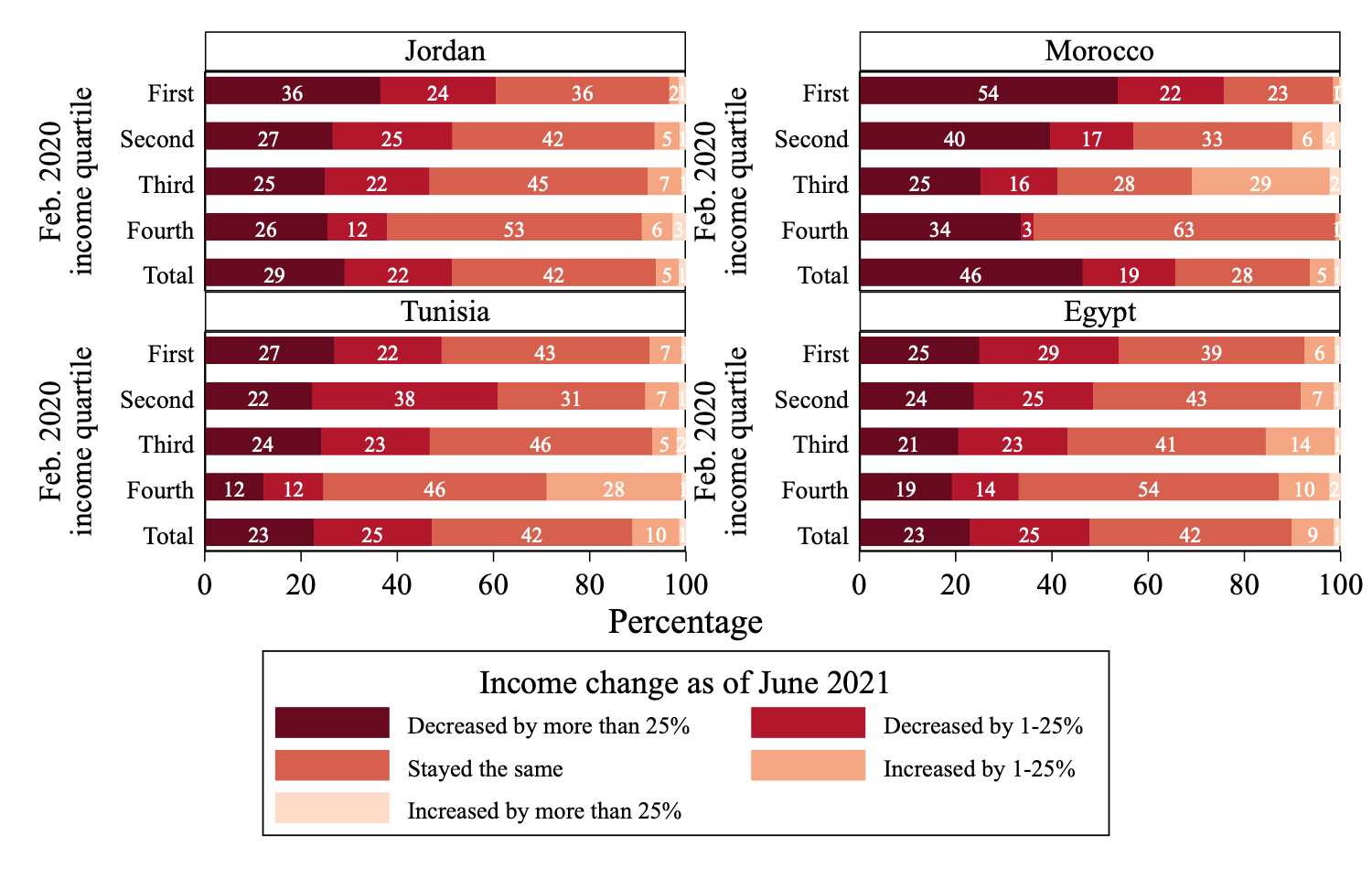
As Figure 2 shows, household income losses were highest for the households that were poorest pre-pandemic, confirming the adverse effects of the pandemic on poverty and inequality.
Figure 2: Changes in household income from February 2020 to June 2021 (percentage of households), by country and February 2020 income quartile
Source: Krafft et al (2022), based on COVID-19 MENA Monitor Household Survey in June 2021.
Social support
Social support reached a relatively limited fraction of the population, except in Jordan, where it reached 53% in February and 44% in June 2021. Assistance was generally well-targeted, reaching a higher proportion of lower-income households than higher-income households. But while targeting efficiency improved in Morocco over time, it deteriorated in Egypt.
Targeting of assistance was generally not based on the workers’ vulnerability with respect to labour market status, again with the possible exception of Jordan, which successfully targeted irregular and informal workers.
Firms’ experiences
It appears that firms in Jordan and Morocco were experiencing more difficulty than firms in Egypt and Tunisia due to the Covid-19-induced crisis in the first quarter of 2021. Although the Tunisian economy had the deepest overall downturn in 2020, it appears to have recovered somewhat by the first quarter of 2021 so that the adverse effects on firms were reduced.
The downturn in Egypt appears to be shallower than in the other countries, sparing Egyptian firms the worst of the negative outcomes. Yet in all countries, there is a clear need for continuing support, especially targeted to the most affected industries and firms, as the economic effects of Covid-19 continue to affect micro, small and medium enterprises.
Support for firms
Although policies were instituted in all four countries to support firms through the crisis, the reach of these policies appears to have been limited. A half to three-quarters of small and medium enterprises reported they had not applied for or received any government assistance.
The most common type of support received (and needed) in all four countries was business loans, but firms in Morocco and Tunisia also report needing (and sometimes receiving) salary subsidies. A substantial proportion of firms in all four countries also expressed the need for reduced or delayed taxes.
Further reading
Krafft, Caroline, Ragui Assaad and Mohamed Ali Marouani (2021) ‘The Impact of COVID-19 on Middle Eastern and North African Labor Markets: A Focus on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises’, ERF Policy Brief No. 60.
Krafft, Caroline, Ragui Assaad and Mohamed Ali Marouani (2022) ‘The Impact of COVID-19 on Middle Eastern and North African Labor Markets: Employment Recovering, but Income Losses Persisting’, ERF Policy Brief No. 73.
OAMDI (2021a) COVID-19 MENA Monitor Household Survey (CCMMHH), Version 4.0 of the Licensed Data Files, ERF.
OAMDI. (2021b). COVID-19 MENA Monitor Enterprise Survey (CCMMENT), Version 3.0 of the Licensed Data Files, ERF.