In a nutshell
A return of the level of Palestinian employment in Israel to its pre-intifada level improves households’ incomes in the West Bank and their access to food.
To match the higher demand associated with more employment of Palestinian labour in Israel, both imports and the supply of domestic output to the domestic market increase: hence the availability of food in the West Bank improves.
From a policy perspective, the Palestinian National Authority may seek with the Israeli authorities an increased Palestinian employment in Israel to improve household welfare and food security in the West Bank.
The conflict between Israel and Palestine attracts substantial media attention for its violence, historical background and political developments. But the economy-wide implications of different policies in Palestine, especially those related to labour mobility, are understudied.
Our research examines various policy options focusing on the labour market with the aim of achieving faster economic growth and improved food security in the West Bank.
We use a computable general equilibrium model calibrated to a unique database for the West Bank to simulate a return of Palestinian employment in Israel to its pre-intifada level of 1999. This corresponds to an increase in the number of Palestinian workers in Israel by 36% compared with its level in the base year of 2011.
We assess the effects on the whole economy and the implications for food availability and consumption. The results show a GDP increase by 3.6% in real terms and an improvement in the welfare of West Bank’s households by 5.5% on average.
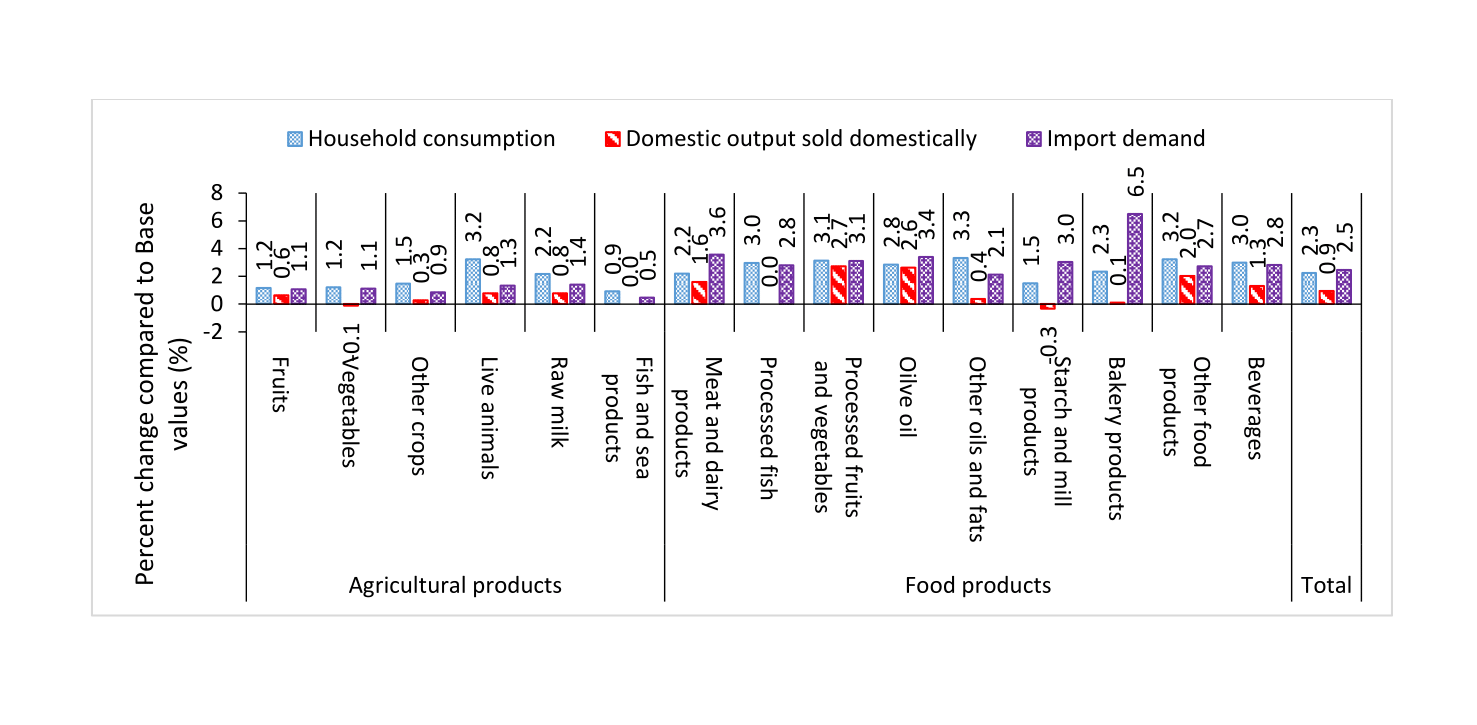
Household consumption of agricultural and food products increases on average by 2.3%. The availability of agricultural and food products in the domestic market increases as import demand rises on average by 2.5% and domestic output sold domestically by 0.9% (see Figure 1).
By contrast, reducing Palestinian employment in Israel by 36% leads to a contraction of the West Bank economy and welfare losses for Palestinian households.
Consumption of agricultural and food products decreases on average by 2.2%. The availability of food and agricultural products drops, as import demand declines by 2.3% and domestic output sold domestically decreases by 0.8%.
In light of these results and the limited development options in the Palestinian territories, the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) may seek increased employment of Palestinian workers in Israel, as a ‘second-best’ policy, in order to improve household welfare and food security.
Increased employment of Palestinian labour in Israel and the associated large inflow of additional labour income from Israel have ‘Dutch disease’ effects, causing the competitiveness of the Palestinian export sector to decline, including agricultural and food exports.
Therefore, the PNA may consider introducing a tax on Palestinian workers employed in Israel. This may raise revenue that can be used to provide incentives for local producers, including farmers, to adopt new production technologies and restore their competitiveness on international markets.
Further reading
Johanes Agbahey, Khalid Siddig, Harald Grethe and Scott McDonald (2018) ‘Labour Exports from Palestine to Israel: A Boon or Bane for the West Bank Economy’, 30th International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE), Vancouver, Canada, July-August 2018 (full paper).
Figure 1:
Changes in food availability when the employment of Palestinians working in Israel returns to its pre-intifada level