In a nutshell
Firms have responded to increased competitive pressures due to globalisation in
various ways, including the provision of trade credit.
Evidence from how Turkish exporters of textile and clothes responded to the removal of the Multi-Fibre Arrangement (MFA) quotas in 2004 shows that extending trade credit attenuates the price response to increased competition.
Ignoring the trade credit channel leads to an underestimation of the full effects of changes in market competition on exporters.
Firms have responded to increased competitive pressures due to globalisation in various ways. This column suggests another margin of adjustment – provision of trade credit. It shows that extending trade credit attenuates the price response to increased competition. Ignoring the trade credit channel leads to an underestimation of the full effects of changes in market competition on exporters.
Globalisation has increased competitive pressures on firms and forced them to change the way they do business. Firms have responded by dropping prices, upgrading quality or adjusting their product portfolio. In our recent study, we point out another margin of adjustment – provision of trade credit (Demir and Javorcik, 2018).
In the international trade context, provision of trade credit is known as open account terms. Under open account, goods are shipped and delivered before payment is due, which is typically in 30, 60 or 90 days after delivery. This option is advantageous to the importer in terms of cash flow and security, but it is less beneficial to the exporter, who bears the financing costs and the risk of non-payment.
The International Trade Administration of the US Department of Commerce advises exporters that provision of trade credit ‘may help win customers in competitive markets’ and that ‘exporters who are reluctant to extend credit may face the possibility of the loss of the sale to their competitors’.
Ignoring the trade credit channel means underestimating the impact of competition
In our study, we use a simple model to illustrate the impact of increased competition on the choice of export financing terms and prices. The model predicts that the share of exports on trade credit increases and the average price decreases with the level of market competition faced by exporters.
Moreover, the price adjustment is attenuated by trade credit provision. This happens because the optimal price under trade credit is higher, thus switching from other financing terms to providing trade credit generates a dampening effect on the price response. These predictions imply that ignoring the trade credit channel will lead to underestimation of the full effects of competitive shocks on exporters.
Exploiting an exogenous shock to competition
In our empirical analysis, we exploit a quasi-natural experiment – the removal of the Multi-Fibre Arrangement (MFA) quotas that governed global trade in textiles and clothing until the end of 2004.
During the period from 1993 to 2003, Turkey and China were the leading exporters of textiles and clothing to the European Union (EU). Since Turkey formed a customs union with the EU in 1996, Turkish exports had not been subject to any quota restrictions in the European market. Thus, removal of MFA quota restrictions on China on 1 January 2005 constituted a large shock to competition for Turkish exporters of textile and clothes.
Importantly for our purposes, quota fill rates – the proportion of quotas used by the end of a given year – varied from below 10% to 100% in 2004, implying that the MFA quotas were binding only for some, but not for other, products. As higher quota fill rates reflected a greater constraint on Chinese exporters and thus a greater increase in competitive pressures after the quota removal, the shock had a differential impact across products.
We employ detailed data on Turkish exports of MFA products to the EU, disaggregated by the exporting firm, product, destination country, year and financing terms for the period from 2002 to 2007. We compare changes in exports in the pre- and the post-MFA period of products with binding MFA quotas to those with not binding quotas.
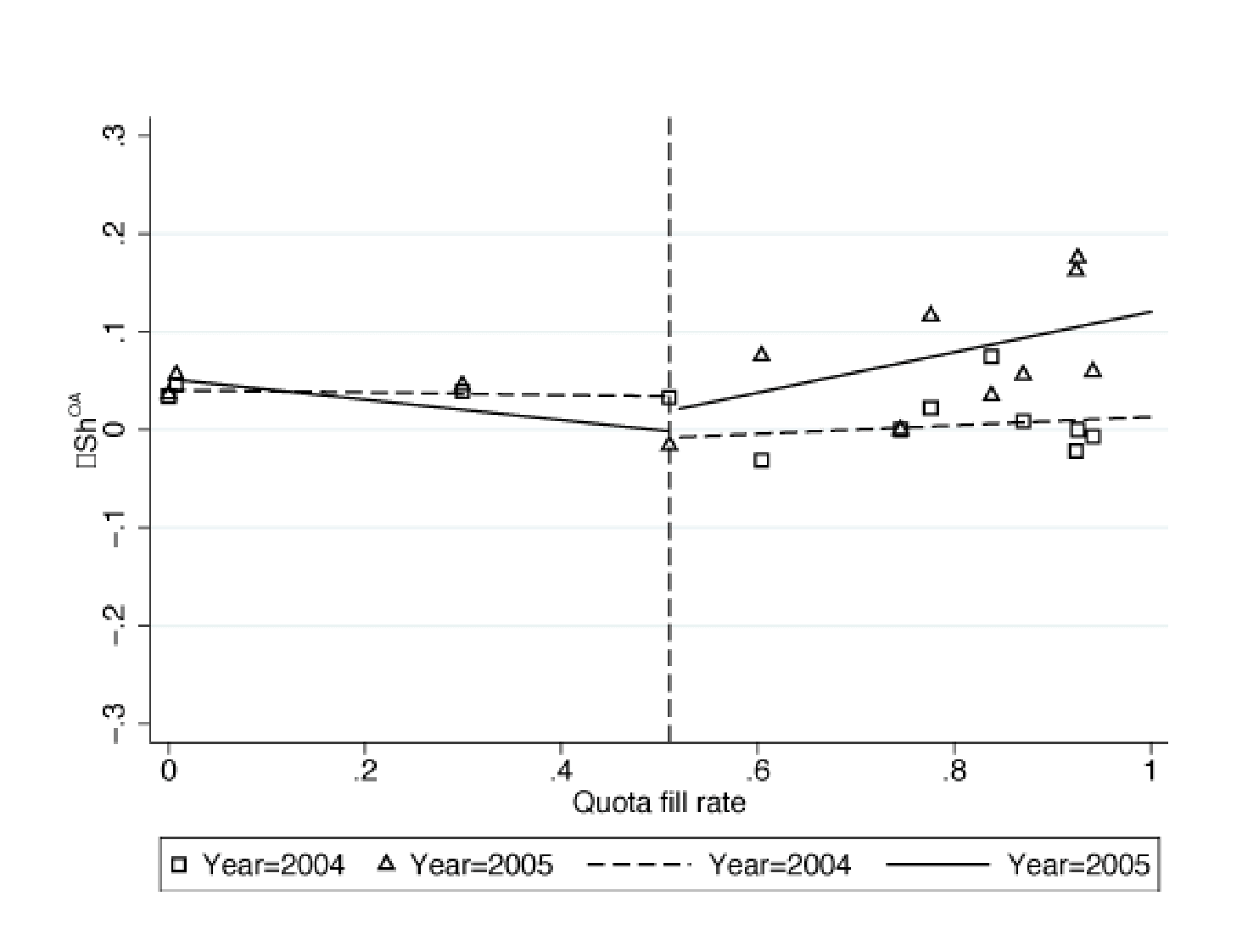
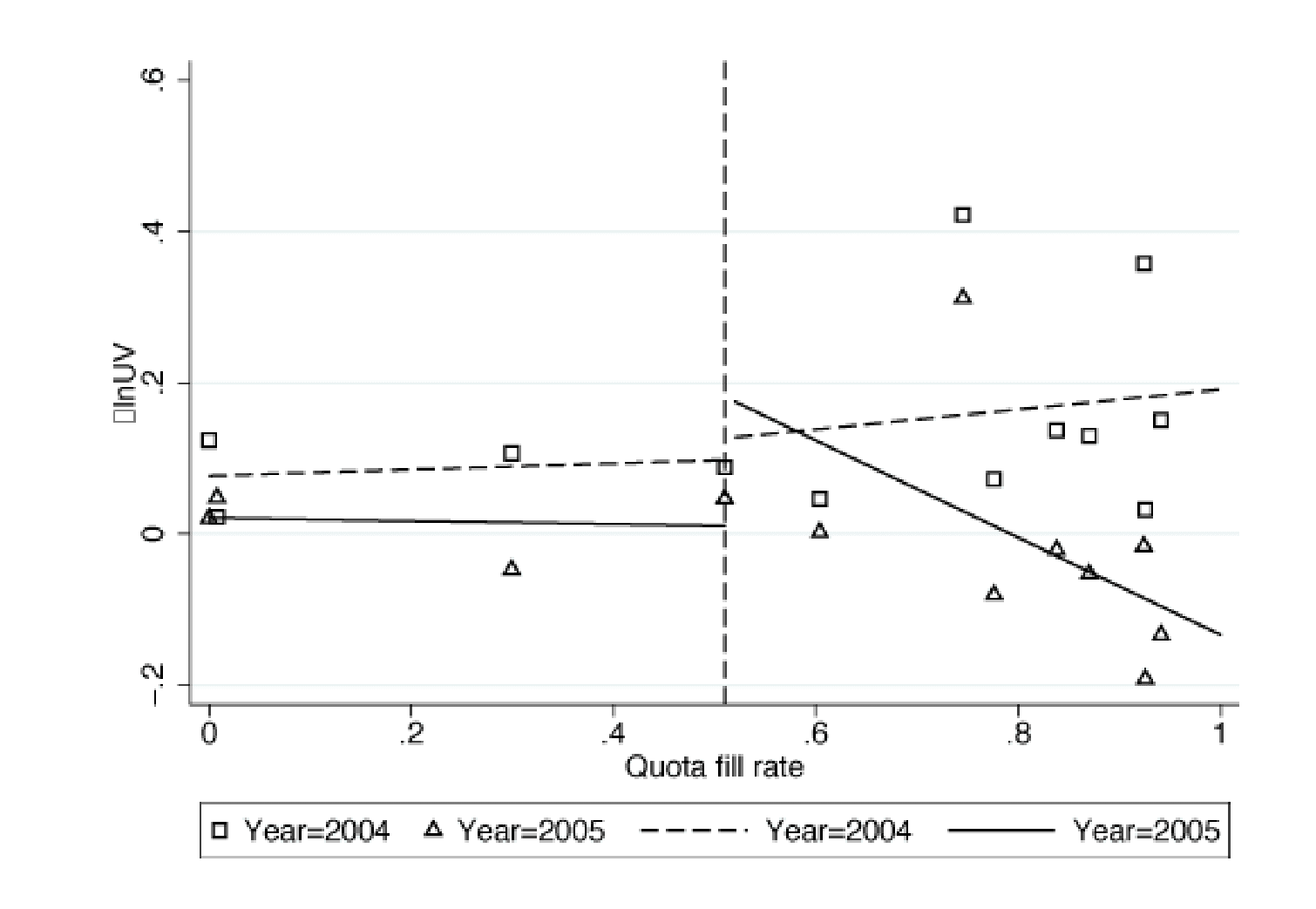
The differential impact of the shock on the two groups of products is visible in Figure 1. The top panel plots the change in the share of exports on trade credit in the post-shock (2005 relative to 2004) and the pre-shock (2004 relative to 2003) periods against the quota fill rates in 2004. The bottom panel repeats the exercise for export prices.
The plots show that changes in the provision of trade credit and unit values for the control products (that is, those with quota fill rates below 50%) stayed flat and close to zero in the post-shock period. In contrast, the affected products (that is, those with quota fill rates above 50%) saw an increase in provision of trade credit and a steep fall in prices in the post-shock period.
These patterns are consistent with the theoretical predictions that Turkish exporters affected by an increase in competitive pressures would respond by extending additional trade credit and lowering prices.
The analysis suggests that Turkey’s exports of MFA products affected by the shock saw a four percentage point larger increase in the share of sales on trade credit and a 7% larger decline in prices compared to the other MFA products destined for the EU market in the post-MFA period.
To investigate the interaction between the two margins of adjustment, we examine whether export flows with a high initial share of sales on trade credit experienced a larger subsequent fall in prices. A high share of sales on trade credit in the pre-shock period means less room to increase trade credit after the shock and hence less room to attenuate the necessary price response by switching financing terms.
Our empirical findings are in line with this hypothesis. Export flows of affected products with no room for further adjustment on the financing side (that is, full reliance on trade credit before the shock) experienced about a 12% larger fall in prices relative to flows with no reliance on trade credit before the shock.
Conclusions
Our study has two implications. First, it highlights the importance of considering the full terms of the transaction, including the financing part, rather than just focusing on price effects, for a complete understanding of the effects of a competitive shock on firms.
Second, our results rationalise why many governments are engaged in provision of trade financing by establishing import-export banks.
Further reading
Demir, Banu, and Beata Javorcik (2018) ‘Don’t Throw in the Towel, Throw in Trade Credit!’, Journal of International Economics 111: 177-89.
A longer version of this article was first published on VoxEU.org – read the original article.
Figure 1 Change in provision of trade credit and prices before and after the end of the MFA
Notes: DShOA denotes the annual change in the share of exports on trade credit (OA terms). DlnUV denotes the annual change in the logarithm of unit values. In the left (right) panel, a marker represents average DShOA (DlnUV) over firms, products and destination countries for a given quota-fill rate and year. Lines represent fitted values of (unconditional) linear predictions. The vertical lines represent the quota fill rate of 0.5 as of 2004.