In a nutshell
Upgrading congested arteries of two-lane paved roads into four-lane carriageways is a cost-effective investment with a high rate of return for middle-income countries.
The cost of an average shipment over a high-capacity expressway is 70% lower than over single-lane roads: lower freight costs imply higher exports.
Reduced travel times from better roads have a positive effect on trade between domestic regions – and the impact is as important for the service sector as for manufacturing industries.
Transport plays a vital role in modern market economies by enabling domestic and international trade. High transport costs impede market access in isolated regions, in terms of firms’ ability both to sell goods and to buy the inputs they require. Thus, investment in transport infrastructure can improve growth prospects by facilitating trade.
This is an area in which the Middle Eastern and North African (MENA) region has substantial investment needs. According to the 2013 EBRD and World Bank Enterprise Surveys, the percentage of firms that identify transport as a major constraint in the region is 21%, several percentage points higher than the worldwide average (EBRD, 2017).
How should authorities in the region go about prioritising various projects in order to improve the connectivity of their firms and people? The experience of Turkey from a major programme of road upgrades since the early 2000s offers useful insights.
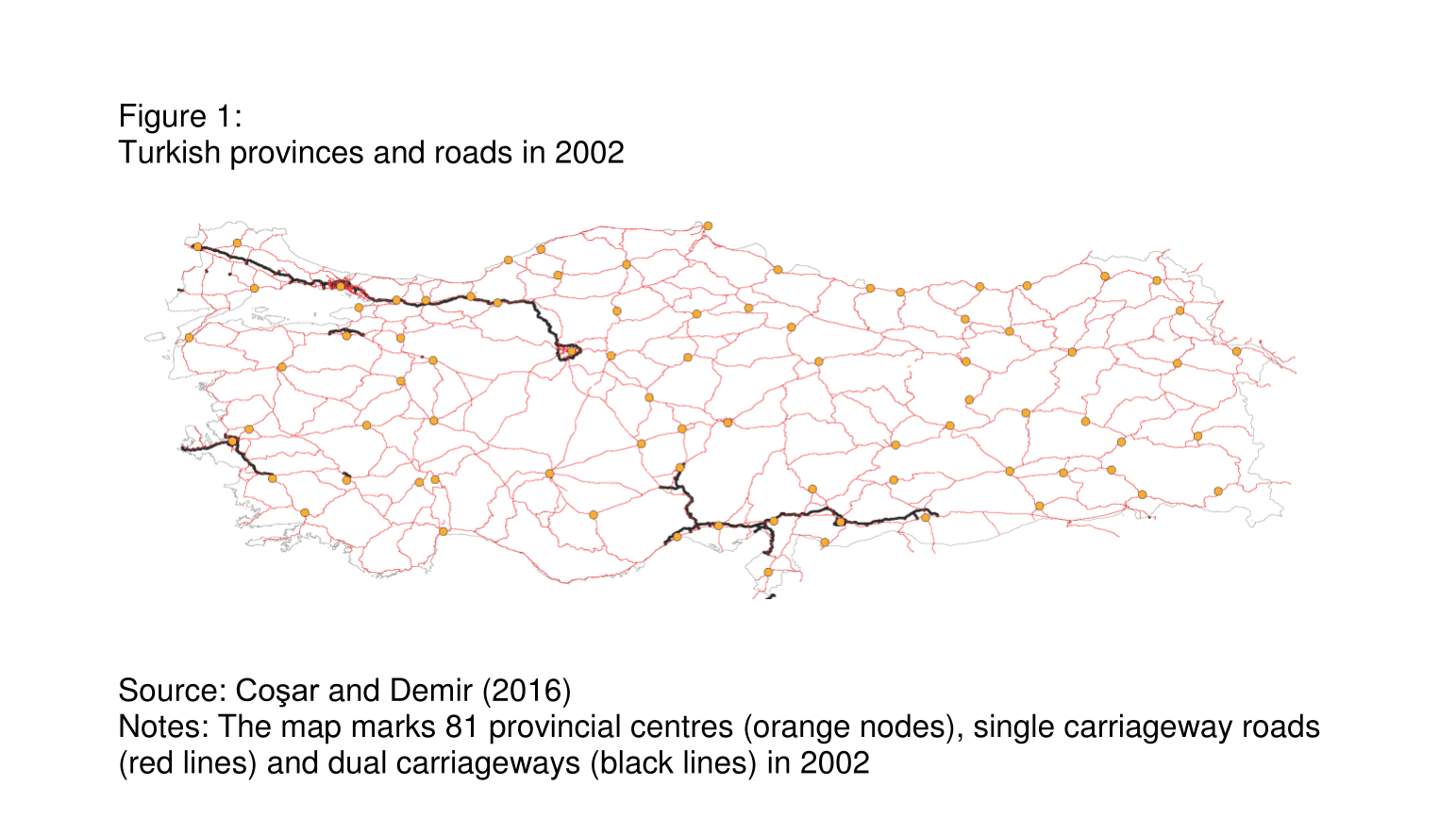
As in many MENA countries, Turkey had an extensive network of paved inter-provincial roads prior to the 2000s (the red lines in Figure 1). But since divided multi-lane highways made up only a small percentage of that network (the black lines in Figure 1), the capacity of these roads had long been considered inadequate.
In order to relieve congestion and reduce the high rate of road accidents, the authorities launched a large-scale programme of public investment in 2002. Subsequent construction converted a sizable fraction of existing single carriageways (two-lane undivided roads) into dual carriageways (divided four-lane expressways – see Figure 2).
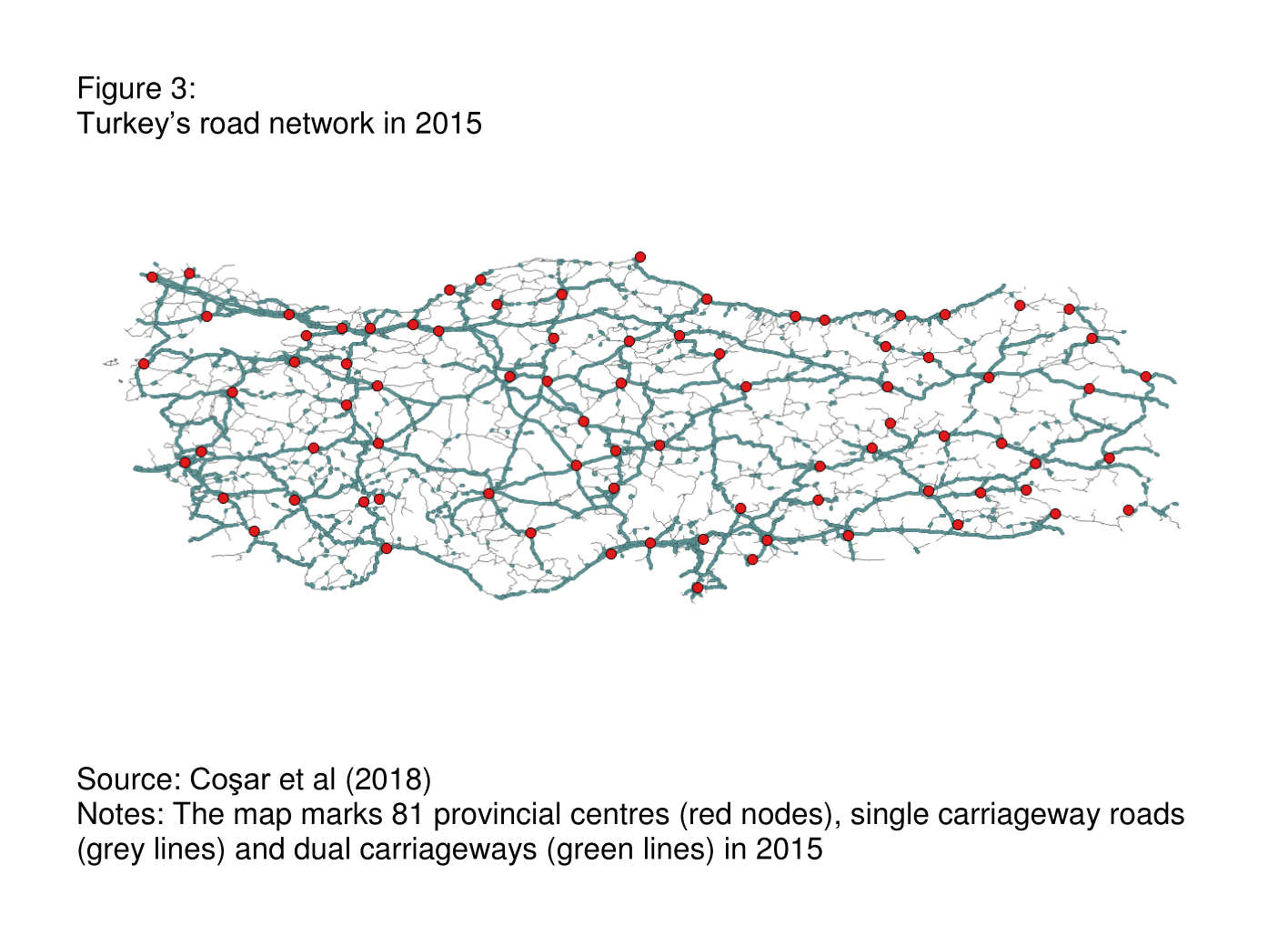
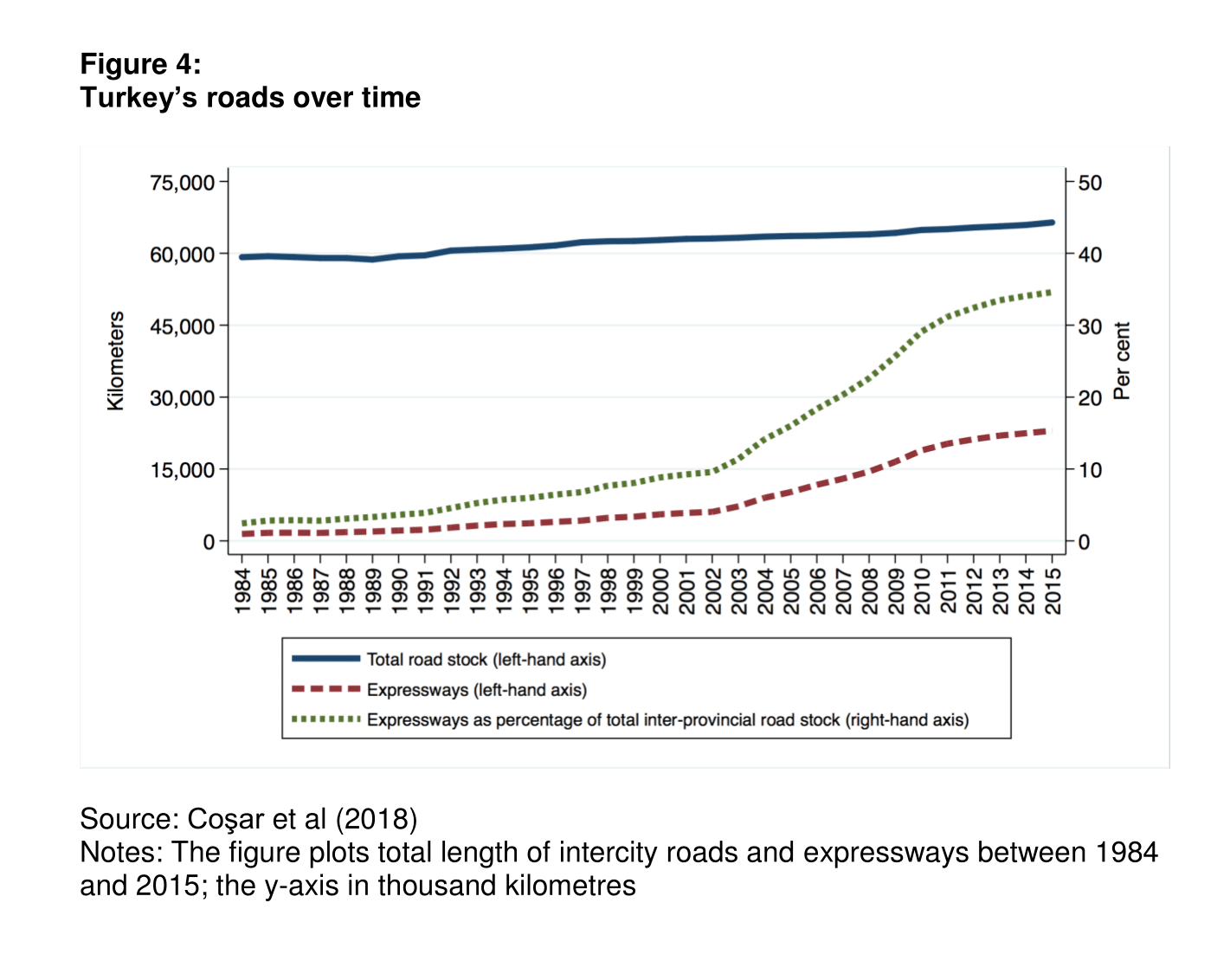
As a result, the length of dual carriageways increased by more than threefold during the period from 2003 to 2015, while total road stock remained essentially unchanged (see Figures 3 and 4). The increase in capacity has allowed vehicles to travel more reliably at higher speeds, reducing accident rates and making arrival times more predictable.
A key policy-relevant aspect of this investment is the choice of expanding the lane capacity of existing roads rather than constructing highways. According to cost studies from Turkey, 1km of a new highway costs between $4 million and $8 million whereas expanding an existing two-lane road into a divided four-lane dual carriageway costs around $1 million (Gerçek, 2001).
Evidence from the United States shows that adding new lanes to an existing freeway can range between $2 million and $10 million per lane-mile while the cost of constructing a new freeway can range between $5 million and $20 million per lane-mile (Texas A&M Transportation Institute). For countries that have a decent network of paved roads to begin with, upgrading them to a dual carriageway is thus a cost-effective intermediate step.
Besides its cost efficiency, what has been the quantitative impact of this investment on international and domestic trade? We address this question in two empirical studies: in Coşar and Demir (2016) and Coşar et al (2018), we use data on sectoral inter-national trade of Turkish provinces and intra-national trade across Turkish provinces, respectively, to estimate the response to improved road connectivity within the country.
Our first result shows that the cost of an average shipment over a high-capacity expressway is about 70% lower than it is over single-lane roads. Lower freight costs imply higher exports.
Taking the average increase, and the cost of building a kilometre of dual carriageway at the reported $1.1 million, each dollar spent on quality-improving investment in transport infrastructure generates a 10-year discounted stream of export flows of between $0.7 and $2, depending on the discount factor used of between 5% and 15%. This is a substantial boost to exports.
Moreover, the increase is more pronounced in time-sensitive industries such as machinery, chemicals and electronics. This highlights the importance of domestic transport infrastructure in moving goods from factories to ports in a timely and predictable fashion.
Our findings have important implications for growth: efficient logistics in time-sensitive goods enable countries to take part in global supply chains and exploit their comparative advantages. Due to its geographically advantageous position between Europe and the fast-growing East and South East Asian economies, the MENA region stands to gain from this mechanism.
Our results on domestic trade reveal further interesting patterns. The quantitative impact of road improvements on domestic trade is economically and statistically significant. In particular, a one-hour reduction in travel times between two provinces increases inter-industry bilateral trade by about 5%.
But this figure masks important qualitative patterns. Before the roads were upgraded, 43% of all potential province-to-province links in Turkey were unexploited, with zero trade. After the investment, most links were realised with just 3% left without any trade.
The result is increased integration of markets within the country. Among all provinces, those that were previously most isolated show the largest gains. This also manifests itself as increased employment and sales in these regions.
We also find positive effects for the service sector. This implies that the effects of reduced travel times between domestic regions on industries involving the movement of people are as important as their effects on those producing goods. To the extent that this translates into higher frequency of economic interactions as well as social interactions, it may prove to be a unifying force that contributes to cohesion within countries.
Note that our analysis leaves out several important benefits such as the value of time and fuel savings, as well as the value of decreased accident and mortality rates. Even without taking these into account, upgrading congested arteries of two-lane paved roads into four-lane carriageways seems to be a cost-effective investment with a high rate of return for middle-income countries.
Further reading
Coşar, AK, and B Demir (2016) ‘Domestic Road Infrastructure and International Trade: Evidence from Turkey’, Journal of Development Economics 118.
Coşar, AK, B Demir and N Young (2018) ‘Road Capacity, Domestic Trade and Regional Outcomes’, Working Paper.
EBRD (2017) Transition Report 2017/2018: Infrastructure and Growth, Chapter 3, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
Gerçek, H (2001. ‘Otoyolların mali ve ekonomik değerlendirilmesi’, 06/2001, s. 89-100, 5. Ulaştırma Kongresi, TMMOB, İstanbul Şubesi, İstanbul, 30.05.2001 – 01.06.2001 (accessed on 14 January 2018).
Texas A&M Transportation Institute (2018) ‘Adding New Lanes or Roads’ (accessed on 14 January 2018).