In a nutshell
In Egypt today, the labour market has become increasingly inhospitable for women, with the shirking role of the public sector as a major employer in recent decades. Despite this worrying trend, female jobs in ICT are on the rise, giving cause for optimism.
On an economy-wide level, female employment in ICT jobs has been growing at a compound rate of 6.4% per year, compared with a decline of 1% per year for non-ICT jobs, making the share of ICT jobs among working women more than doubling from 1% of female employment in 2009 to 2.3% in 2021.
Men and women in ICT jobs have different occupations. In 2021, nearly half of ICT jobs held by women in the private sector were for data entry clerks, receptionists and call center operators, compared with only 16% for men, who are more likely to work as technical assistants, in sales, or in blue-collar positions.
More can be done to realise the promise of ICT employment, especially for Egyptian women. Cultivating an attractive investment environment for international firms with broad training programmes is critical.
With the increasing withdrawal of the public sector as a major employer in Egypt, the Egyptian labour market has become increasingly inhospitable for women. Female employment rates declined steadily from 19.5% in 2009 to 13.7% in 2021.
Women’s employment has been falling in absolute terms at a rate of 1.1% per year from 2009 to 2021, while the female working-age population has been increasing at 2.5% annually. Information and communication technology (ICT) jobs are a major bright spot in this bleak landscape.
According to a recent report on Egypt’s ICT jobs, ICT employment for women has been growing much faster than in other segments of the economy and much faster than for men (Selwaness, Assaad and El Sayed, 2023). The report defines ICT jobs as all jobs in ICT industries and jobs in ICT occupations in non-ICT sectors. Although these jobs still make up a small percentage of overall employment in Egypt, their share has grown from 1.4% in 2009 to 1.9% in 2021.
Is ICT employment in Egypt making enough space for women?
In fact, the share of ICT jobs in total employment occupied by women has risen from 1% in 2009 to 2.3% in 2021, a much more rapid increase than for men.
The contrast between the growth of female employment in ICT versus other segments of the Egyptian economy is even more impressive when one examines growth rates. Economywide, female employment in ICT jobs has grown at a compound rate of 6.4% per annum compared to a decline of 1% per annum for non-ICT jobs.
The contrast is even more significant in the private sector, where female ICT employment has grown at an explosive 10% per annum, relative to a decline of 1.4% per annum in non-ICT jobs. ICT jobs have also been growing faster than other jobs for men, but the contrast is not as large as for women.
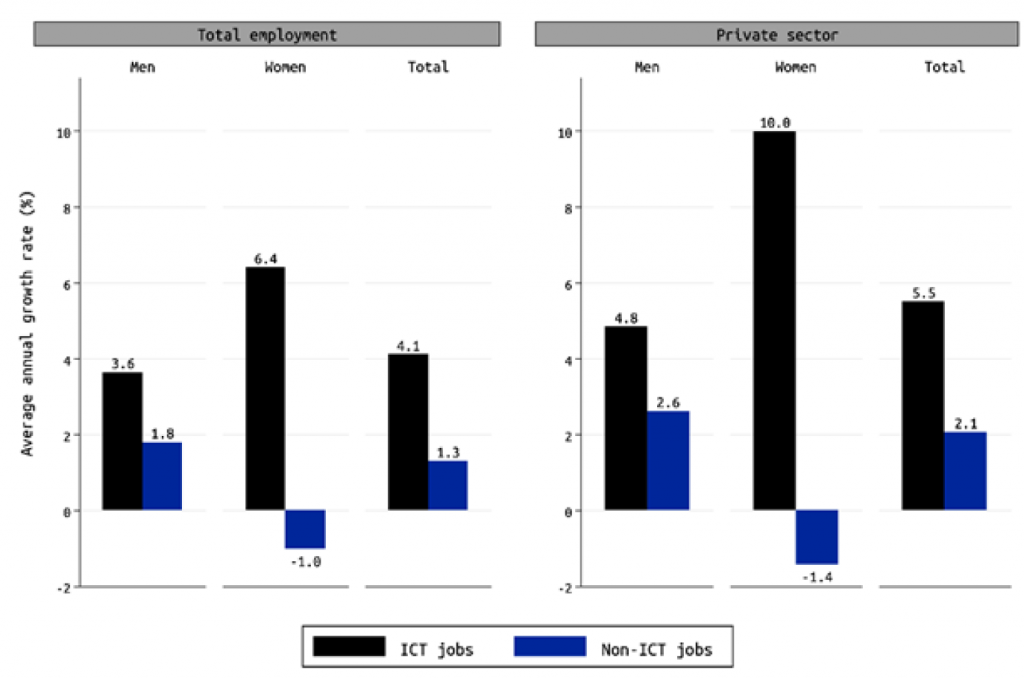
Source: Selwaness, Assaad, and El Sayed (2023)
The occupational structure within Egypt’s ICT sector is quite different for men and women. In 2021, nearly half of women in ICT jobs in the private sector were in data entry, receptionists, and call centre operator jobs, compared to only 16% for men.
In contrast, a third of men in ICT were in technical assistant and sales jobs, compared to only 19% for women. Men are also much more likely than women to be in blue-collar ICT occupations such as electronic fitters, mechanics, and assemblers.
Surprisingly, the proportion of men and women in ICT jobs who have professional occupations such as computer professionals and engineers is almost equal (18-20%).
The report indicates that recruits into ICT jobs are increasingly more likely to be educated at the tertiary level, with the proportion of workers with tertiary education increasing from 43% in 2009 to 63% in 2021 in the private sector.
The ratio of workers in Egypt’s ICT jobs with ICT-specialised educational credentials is also growing, especially among ICT workers with tertiary education (from 28% in 2009 to 37% in 2021).
Conditions for ICT workers have not improved over time
Despite the rapid growth of ICT employment, conditions for ICT workers have not necessarily improved over time. Like in the rest of the economy (Amer, Selwaness, and Zaki 2021; Selwaness and Ehab 2022), the proportion of ICT jobs providing social insurance coverage, i.e., formality, has been declining, and the decline has been steeper for women than for men.
The peak of social insurance coverage in ICT jobs was reached around 2014 when 67% of men and 60% of women were covered. Coverage rates have fallen since then, reaching 59% for men and 47% for women in 2021.
Similarly, wage rates in ICT employment in Egypt are not much higher than the average in the rest of the Egyptian economy for either men or women. Like other wages in the Egyptian economy, they have not been keeping up with inflation and have been declining in real terms over time. These challenges can hamper the potential role of ICT in boosting women’s employment.
Government efforts to promote ICT employment growth in Egypt
The Egyptian Government has been prioritising Egypt’s ICT jobs in its development plans. It launched the ‘Digital Egypt’ strategy to promote digital transformation by providing e-services and increasing digital inclusion.
The National Structural Reform Programme (NSRP) aims to substantially increase Egypt’s digital services exports by 15% annually and double services and digital goods exports from $4 billion in 2020 to $8 billion by 2024.
To further promote the growth of service exports, the NSRP plans to increase Egypt’s attractiveness to international Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) companies to set up their operations in Egypt through well-serviced specialised industrial zones.
The NSRP programme aims to create 120,000-140,000 jobs by 2024 and increase the number of beneficiaries of different education and training programmes provided by the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology and its affiliated institutions by an average of 20-25% yearly (MPED 2022).
More can be done to realise the promise of ICT employment for women. Further efforts are necessary to improve the investment climate for both domestic and international ICT firms. Measures should encourage international training organisations with ties to global IT firms to set up shops in Egypt and train Egyptian workers, especially women, for remote jobs in the worldwide IT industry.
Training programmes should capitalise on increased global demand in data analytics and artificial intelligence to enable the participation of Egyptian workers in the global IT industry without leaving home.
Finally, the Egyptian Government needs to develop mechanisms to ensure that Egypt’s ICT workers and remote and platform workers have decent working conditions and adequate social protection.
This article was first published at the Open Access Government. The original version is here.
Further readings
Amer, Mona, Irene Selwaness, and Chahir Zaki. 2021. “Labour Market Vulnerability and Patterns of Economic Growth: The Case of Egypt.” In Regional Report on Jobs and Growth in North Africa 2020. Cairo, Egypt: International Labor Organization.
MPED. 2022. “The National Programme for Structural Reforms: The Second Stage of the National Programme for Economic and Social Reform.”
Selwaness, Irene, Ragui Assaad, and Mona El Sayed. 2023. “The Promise of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Jobs in Egypt.” National Forum on the Future of Work in Egypt. GIZ and Economic Research Forum.
Selwaness, Irene, and Maye Ehab. 2022. “Social Protection and Vulnerability in Egypt: A Gendered Analysis.” In The Egyptian Labor Market: A Focus on Gender and Economic Vulnerability, edited by Caroline Krafft and Ragui Assaad. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.



