In a nutshell
The protocol regulating economic relations between Palestine and Israel no longer addresses challenges facing the Palestinian economy, such as disrupted agricultural trade, food shortages and surges in food prices.
Simulating alternative trade policies in a future sovereign Palestinian state shows that a liberal and non-discriminatory trade regime provides the highest benefits.
Introducing new tariffs on agricultural products imported from Israel would reduce food availability in the West Bank, indicating the benefits of concluding a trade agreement with Israel after leaving the customs union.
Palestine’s trade in goods and services in general – and its trade in agricultural and food products in particular – have been disrupted by the political conflict with Israel. Due to Israeli policies, the Palestinian economy has been isolated and is barely integrated with international markets. Closures erected by the Israeli security forces in an unpredictable manner and curfews declared on short notice have considerably increased transaction costs of trading in the Palestinian territories.
Moreover, the protocol on economic agreement signed between Israel and the Palestinian Liberation Organization in 1994 has formalised a customs and monetary union between the Israeli and Palestinian economies based on Israeli trade and monetary policies. Accordingly, the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) has been left with limited policy space for setting tariffs and choosing a monetary regime that suits Palestinian interests.
While the initial protocol was designed for a transitory period of five years, it still governs Palestinian economic relations with Israel and the rest of the world two decades after it was supposed to give way to a permanent agreement. Realising that the protocol is outdated and that it no longer addresses the challenges facing the Palestinian economy, several voices have called for its revision.
A group of Palestinian and Israeli scholars and officials has suggested that the PNA should be given full control over trade and monetary policies. In such a context, two key questions arise:
- What is the optimal trade regime for a future Palestinian state?
- What are the implications for food security?
Our research addresses these questions using a computable general equilibrium model calibrated to a unique database for the West Bank.
Our results show that a liberal and non-discriminatory policy – one that eliminates or reduces tariffs for all trading partners – outperforms the other trade regimes assessed in terms of household welfare, food security and macroeconomic indicators.
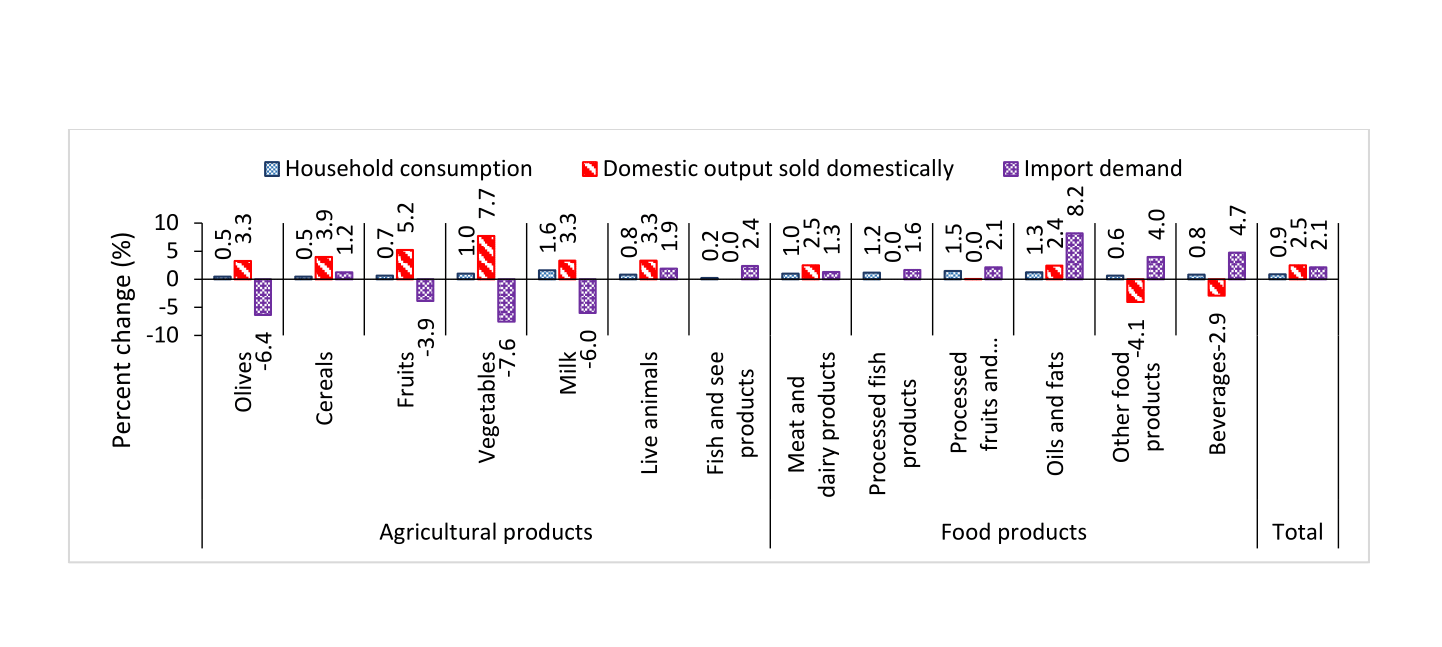
Compared with a continued customs union with Israel, a liberal and non-discriminatory trade policy leads to an increase in household consumption of agricultural and food products of 0.9% on average. This is matched with increases in import demand and domestic output sold domestically by 2.1% and 2.5% on average respectively (see Figure 1). Household welfare increases by 8.0% on average and real GDP grows by 8.3%.
In our assessment of alternative trade regimes, one that introduces new tariffs on imports from Israel (assuming that Israel is treated in a similar way to countries with no current preferential trade agreements with Palestine) would hurt the West Bank economy, with GDP decreasing by 8.4%.
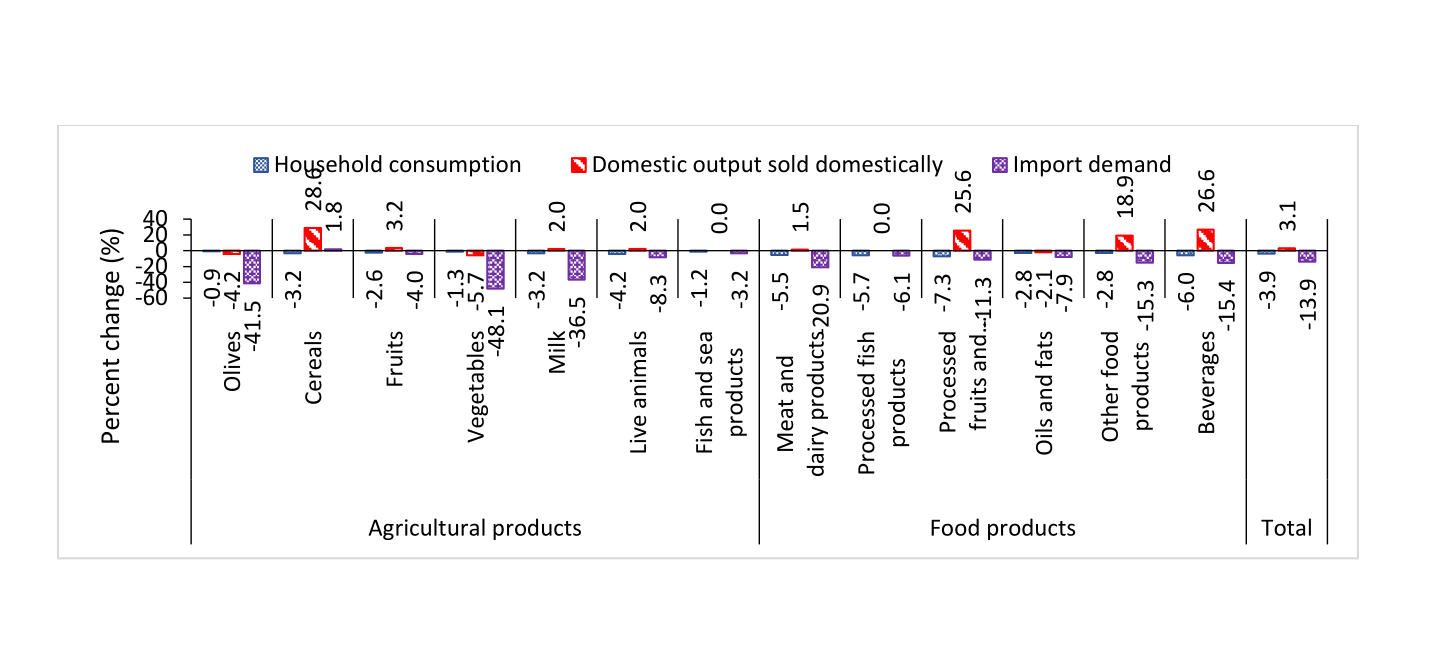
In this scenario, household consumption of agricultural and food products decreases by 3.9% on average. Although the domestic supply of domestically produced commodities increases by 3.1% on average, total supply to the domestic market decreases as import demand declines by 13.9%, compared with a continued customs union with Israel (see Figure 2). Ultimately, household welfare decreases by 7.3% on average.
These findings have two important implications. First, they highlight the trade-off between food sovereignty and food availability using comparative advantages in trade. Imposing new tariffs shields the domestic agricultural and food sectors against import competition. Hence, domestic output increases on average and producer welfare improves. However, as total imports decrease, food availability declines and the average household consumes fewer agricultural and food products. Since, a large proportion of Palestinian households are net consumers of food products, the total welfare effects are negative.
Second, these results pinpoint the significance of imports from Israel to the West Bank. Due to its geographical location and the size of its economy, Israel is likely to remain the main trading partner of the West Bank in the future. Therefore, the PNA may want to keep trade with Israel relatively free in future arrangements.
In conclusion, the PNA may favour a liberal and non-discriminatory trade regime to maximise welfare gains and food security in the West Bank. It may also consider keeping trade with Israel relatively free, as Israel is likely to remain the largest trading partner of the West Bank in the future.
Further reading
Agbahey, Johanes, Khalid Siddig, Harald Grethe and Jonas Luckmann (2018)
‘Trade Policy in a Sovereign Palestinian State: What are the Options in a Final Settlement?’, ERF Working Paper No. 1242.
Figure 1:
Change in consumption and availability of food and agricultural products in a liberal and non-discriminatory trade regime, compared to a continued customs union
Figure 2:
Change in consumption and availability of food and agricultural products in case of high tariffs on imports from Israel, compared to a continued customs union