In a nutshell
Pandemics and natural disasters both have detrimental effects on growth during the emergency stage, depress both supply and demand, and require substantial resources to mitigate the negative consequences for economic activity.
Wars cause debt-to-GDP ratios to rise the most; the ratio increases more moderately for natural disasters because output growth picks up afterwards; the ratio tends to be higher in economies that enter restructuring episodes, but drops sharply thereafter.
We can expect economic growth to pick up as the pandemic wanes; despite this, most developing countries will be saddled with long lasting, although modest, increases in debt relative to gross domestic product.
The health and economic impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic are still ravaging the world. If fighting the pandemic is like fighting a war, as economics Nobel laureate Paul Krugman argued, what implications does this ‘war’ have for debt and growth in developing countries?
Our recent study answers that question by examining how debt and economic growth in developing countries evolve before, during, and after the onset of three types of calamities – natural disasters, conflicts, and external debt distress.
Natural disasters
The Covid-19 pandemic shares many traits with large natural disasters in fundamental ways relevant to understanding how public debt and economic growth evolve around these events . Both pandemics and natural disasters are rare and unexpected occurrences, at least in their timing, and neither is directly caused by economic policies. Both result in economic contractions due to disruptions to people’s daily lives, such as their ability to work and carry on normal economic activities.
Still, there are differences between the two: a natural disaster is generally local, whereas a pandemic is global. In addition, certain types of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, are short-lived, while the pandemic’s duration remains uncertain.
But these differences do not take away from our ability to analyse growth and debt dynamics. Pandemics and natural disasters both have detrimental effects on growth during the emergency stage, depress both supply and demand, and require substantial resources to mitigate the negative consequences for economic activity during and immediately after the crisis.
We find that in developing countries, public debt tends to increase to support economic recovery during and after large natural disasters. During the three years following a large natural disaster, growth in public debt is significantly higher than in countries that did not experience a disaster – the counterfactual scenario .
Our estimates indicate that, on average, public debt grew 2.3 to 3.6 percentage points higher during the three years after the disaster compared with unaffected economies. Real GDP growth collapsed in the year of a natural disaster by approximately 1.3 percentage points relative to unaffected economies. Yet during the three years after a natural disaster, economic growth tends to be about 1 percentage point higher in economies recovering from disasters than in other countries.
This finding provides an important empirical regularity that public debt increases after disasters and is likely to do so after this pandemic, possibly to support economic recovery . This finding, based on past data, supports the rationale for increasing public debt during the pandemic and is consistent with higher economic growth as the pandemic subsides.
Armed conflicts
There are several ways that conflicts can hurt the economy: conflicts destroy physical and human capital, disrupt internal social dynamics, cause countries to divert public funds from activities that enhance output, and contribute to dis-saving, leading to economic deterioration.
We find that the evolution of debt and growth is different around armed conflicts. Public debt tends to go up even before armed conflicts and continues to increase after they begin relative to no-conflict economies. Economic growth does not pick up after the onset of conflicts, which suggests that government spending during conflicts might not be used to support economic growth.
Debt distress
Highly indebted developing countries experience lower growth before the onset of debt distress episodes. We define debt distress episodes as those with external debt restructurings. Debt restructuring is a process wherein a country experiencing financial distress and liquidity problems refinances its existing external debt obligations to gain more flexibility in the short term and make its debt load more manageable.
We find that restructurings are costly in terms of output growth. In addition, external debt growth one and two years after the onset of a restructuring is significantly lower than that in the countries that did not restructure by 14 to 26 percentage points.
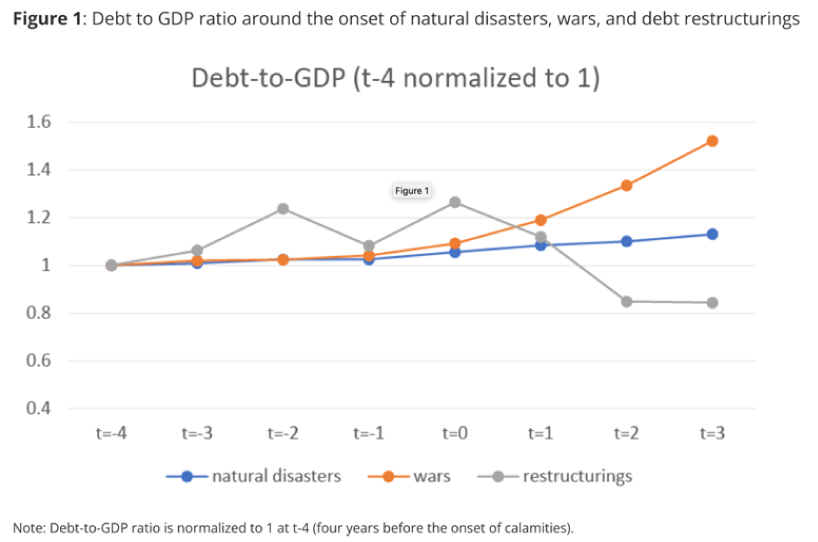
Our findings imply diverging paths of debt-to-GDP ratios, depending on the nature of the calamity. Figure 1 illustrates these stark differences.
Wars caused debt-to-GDP ratios to increase the most. The ratio increases more moderately for natural disasters because output growth picks up after the disasters. Although the debt ratio tends to be higher in economies that enter restructuring episodes before the episode begins, it drops sharply thereafter because countries restructure their external debt or lack access to new external debts.
Figure 1: Debt-to-GDP ratio around the onset of natural disasters, wars and debt restructurings
Given the similarities between natural disasters and the Covid-19 pandemic, our results suggest that we can expect economic growth to pick up as the pandemic wanes. Despite this, most developing countries will be saddled with long lasting, although modest, increases in debt relative to gross domestic product .
We hope that fighting the economic effects of Covid-19 will be similar to reconstruction efforts after natural disasters rather than to fighting a war. But if the increase in debt burden leads to debt distress, the situation will be much more challenging, much like what we see in conflict economies.
This column was originally published in June 2022 on the World Bank’s Let’s Talk Development blog.





