In a nutshell
Governments can conduct cost-effective public procurement by fostering competition: depending on the type of procurement contract, the lowest prices are achieved when there are five to ten bidders.
New entrants are essential to promote competition and reduce procurement costs, but after winning their first contracts, they typically find it difficult to compete with incumbents.
Policy-makers should design policies to encourage participation by new entrants and increase the likelihood that these firms survive in the public procurement market.
Government procurement comprises a substantial part of government spending and often of total GDP too. For example, in 2014, the value of procured goods, services and construction projects in Turkey was approximately US$34 billion, which corresponds to a little over 4% of Turkish GDP.
These figures indicate not only the significance of public procurement auctions for the economy, but also the importance of cost-effectiveness in these auctions. In the following, I describe ways to achieve the lowest possible procurement prices, drawing on my recent research (Tas, 2015, 2017).
Competition is essential for well-functioning and cost-effective public procurement. Accordingly, many international organisations and government authorities take actions to promote it. For example, the World Trade Organization designed its Agreement on Government Procurement ‘to ensure open, fair and transparent conditions of competition in the government procurement markets’.
Competition lowers the probability that a given firm will win a public procurement contract. Firms therefore bid more aggressively to increase their likelihood of winning. Hence, high levels of competition significantly lower procurement costs. In my work, I examine the optimal competitive environment for public procurement auctions by investigating more than half a million of such auctions conducted in Turkey during the period from 2005 to 2012.
I find that there are two key elements to achieving a desirable level of competition: an optimal number of bidders; and the promotion of new entrant firms.
Optimal number of bidders
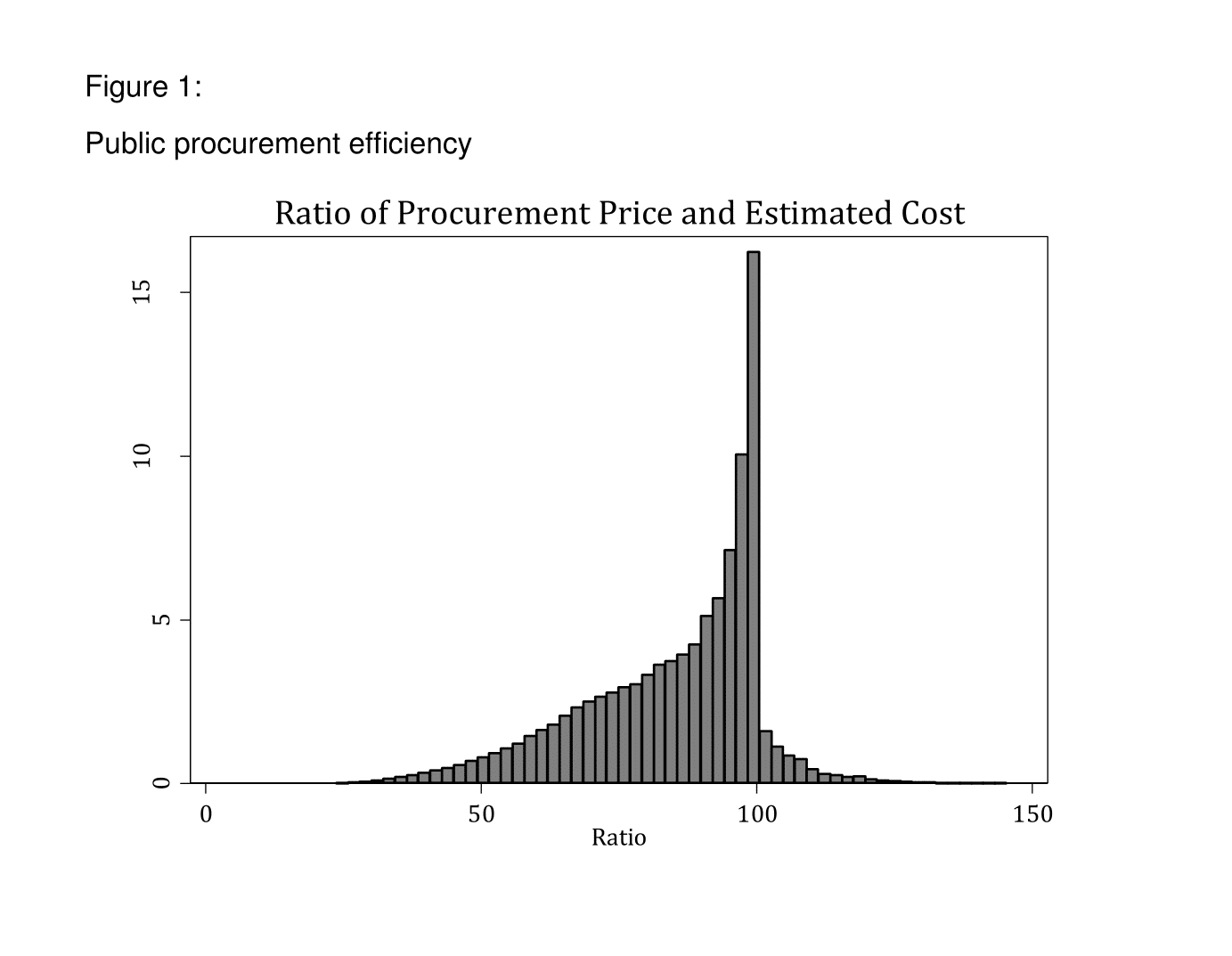
Figure 1 shows the cost-effectiveness of Turkish auctions by presenting the ratio of procurement price over estimated cost in 565,298 auctions. Of these auctions, 7% of procurement prices are above estimated costs. Figure 1 indicates that the efficiency of public procurement auctions varies substantially. Empirical analysis in Tas (2015) shows that the number of firms that submit a bid is the major determinant of procurement efficiency. Auctions with a high number of bidders have significantly lower procurement costs compared with estimated cost.
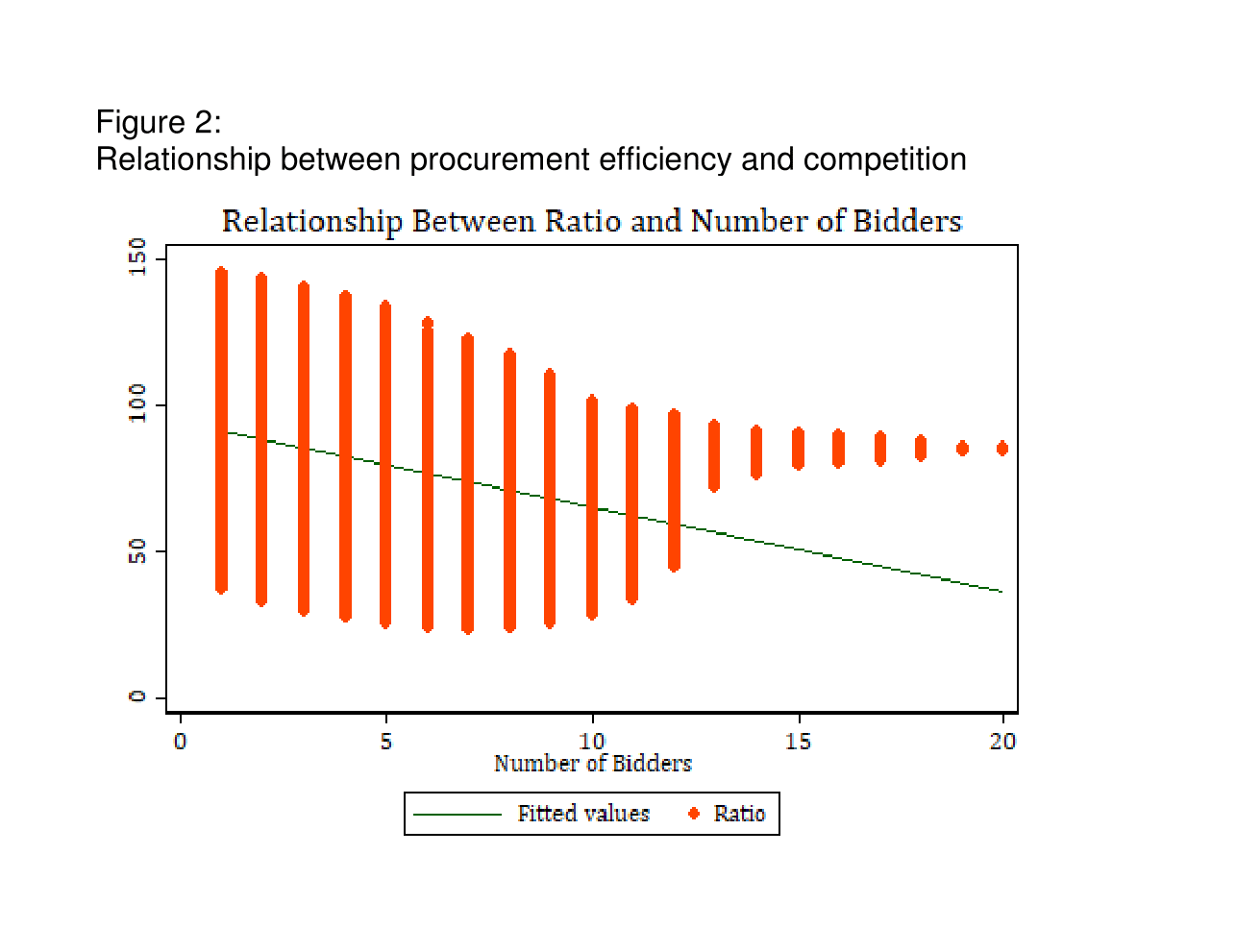
Figure 2 shows the significant and negative relationship between the ratio of procurement price to estimated cost, and the number of bidders.
Theoretical arguments about auctions state that procurement prices might increase when the number of bidders grows beyond a cut-off point (Li and Zheng, 2009). The costs of acquiring information, bid preparation and opportunity costs increase when competition increases. Accordingly, firms tend to bid less aggressively when the competition gets fierce.
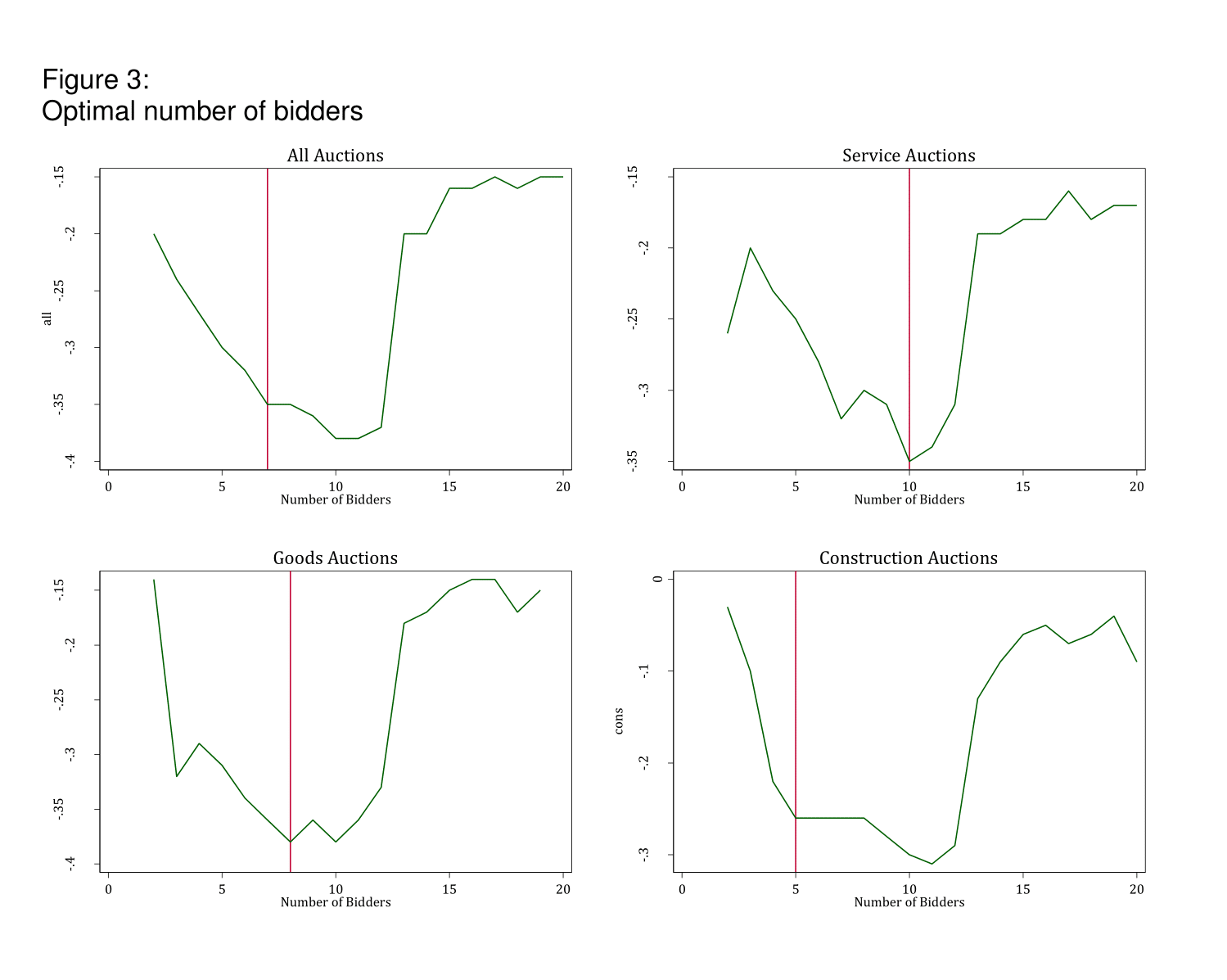
In Tas (2015), I develop a methodology to identify the optimal number of bidders in auctions at which the lowest possible procurement price is achieved. I find that the optimal number of bidders is six when considering all auctions. The optimal level of competition is achieved at ten bidders for service auctions, eight bidders for goods auctions and five bidders for construction auctions.
Figure 3 presents the procurement price compared with non-competitive auctions with just one bidder. The red lines display the number of bidders at which the lowest procurement costs are achieved.
It is particularly notable in Figure 3 that procurement costs rise significantly after the optimal competition levels. For example, procurement prices at auctions with ten bidders are 35% lower than non-competitive auctions with just one bidder.
But an increase in the number of bidders to twelve diminishes the cost-effectiveness of auctions dramatically. Procurement prices at auctions with twelve bidders are 20% lower than non-competitive auctions.
When the number of bidders is above the optimal competition level, procurement prices are higher compared with optimal competition. Increasing competition beyond a certain number of bidders may have an adverse effect on the expected auction price.
This is caused by two major factors that affect bidding behaviour:
- Preparing and submitting bids at public procurement auctions are costly. Bidders need to acquire information and prepare bids according to strict rules.
- The ‘winner’s curse’ becomes more severe as the number of potential bidders increases. This effect is when the winner miscalculates the cost of a contract and loses money in auctions with incomplete information. To avoid the winner’s curse, rational bidders bid less aggressively.
From a practical point of view, these findings have important policy implications. Governments can devise policies to attract an optimal number of bidders that may lead to considerable savings.
My empirical results show that increasing the number of bidders by one participant would on average lead to around 1% lower prices compared with the estimated costs.
Counterfactual analysis shows that if the number of bidders were at the optimal level for all auctions, the average savings per auction would be US$48,457 for service auctions, US$28,445 for goods auctions and US$190,347 for construction auctions.
In Tas (2015), I design a methodology that can be implemented using only procurement prices, estimated costs and number of bidders. Policy-makers can implement this methodology easily using standard econometric tools and software to a wide-range of data sets about public procurement to calculate the optimal level of competition. Policy-makers can employ them as focal points to analyse whether competitive efficiency is achieved in public procurement auctions.
Entrants versus incumbents
One of the major obstacles for viable competition in public procurement is the disadvantage faced by potential new entrants. Entrants promote competition by bidding more aggressively and breaking potentially collusive agreements by incumbents.
In my examination of the bidding behaviour of entrants in Turkish public procurement auctions, I find that promoting entrants can result in significant cost savings by lowering procurement prices. Entrants bid more aggressively and win contracts with significantly lower procurement prices compared with incumbent firms with previous wins.
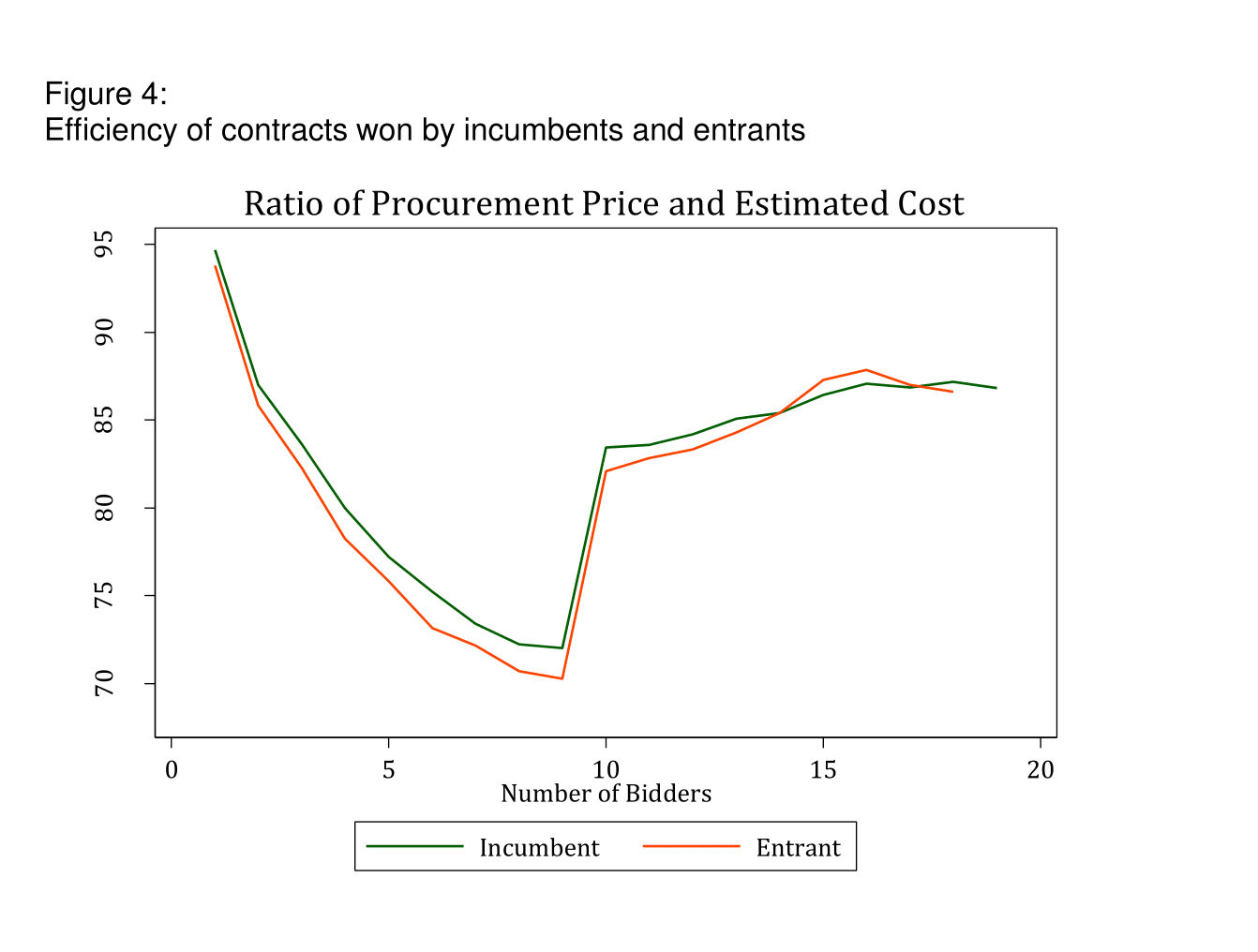
Figure 4 shows the efficiency of public procurement contracts won by incumbent and entrant firms. Procurement prices are significantly lower compared with estimated costs when contracts are won by new entrants. On average, the ratio of procurement price to estimated cost is more than 1% lower in auctions won by entrants. This corresponds to US$3,500 for each auction.
Although entrants promote competition and lower procurement costs, they find it difficult to survive in the public procurement market. For the period from 2006 to 2010, 78,206 unique firms have won at least one contract in 341,771 auctions. There were 50,034 (64%) entrants and 28,172 (36%) incumbents.
Strikingly, I find that 27,820 entrants (56%) did not win another auction after their first win. Entrants struggle to win contracts consistently and leave the market prematurely.
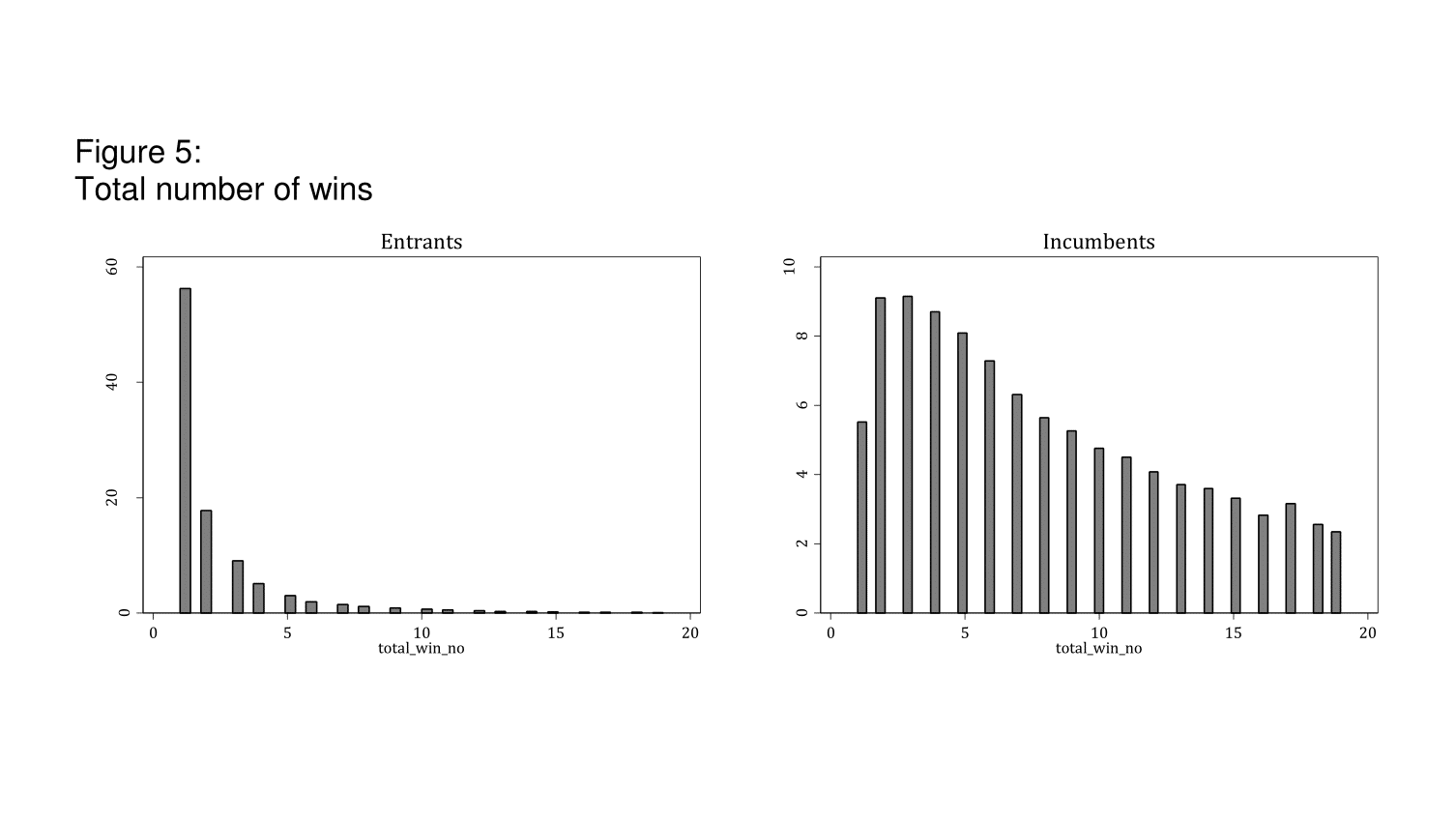
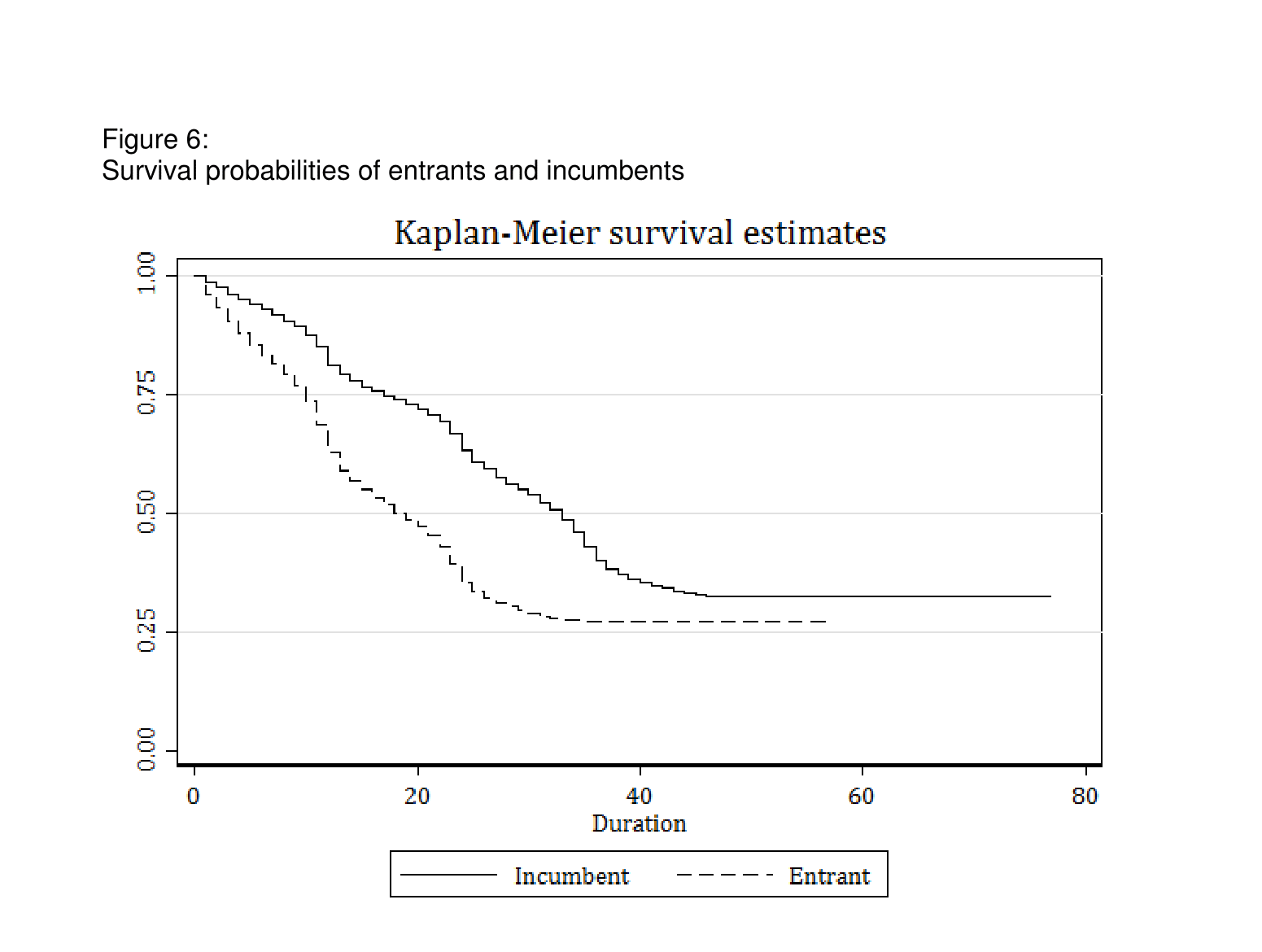
Figure 5 shows the total number of wins by entrant and incumbent firms: only 8% of entrants manage to win more than five contracts. In comparison, 75% of incumbents win more than five contracts. In Tas (2017), I examine the survival probabilities of entrants and incumbents. As Figure 6 shows, entrants’ likelihood of survival is dramatically lower.
I conclude that procurement prices in auctions won by entrants are substantially lower than those in auctions won by incumbents. But entrants struggle to survive in the public procurement market after their first contracts. Accordingly, policy actions to support entrants should be initiated to sustain an increased level of competition.
These empirical findings show that competition is incremental in achieving procurement effectiveness. Nourishing entrant firms is an effective way to enhance competition and decrease procurement costs. On average, contracts won by entrant firms cost US$3,500 less in Turkish public procurement auctions.
These results indicate that policy-makers should cultivate competition and participation by new entrants. Policy actions to support entrant firms should be designed to promote their survival in the public procurement market.
Further reading
Li, T, and X Zheng (2009) ‘Entry and Competition Effects in First-Price Auctions: Theory and Evidence from Procurement Auctions’, Review of Economic Studies 76: 1397-1429.
Tas, BKO (2015) ‘How to Achieve Efficiency in Public Procurement Auctions’,
ERF Working Paper No. 919.
Tas, BKO (2017) ‘Effect of Entrant and Incumbent Bidding on Public Procurement Efficiency’.