In a nutshell
Disaster literacy in Tehran is higher in households with higher income levels, greater trust in Iran’s natural disaster management, a stronger fear of natural disasters, a higher perceived frequency of natural disasters, and greater internet usage.
The wealthier northern districts of Tehran have significantly higher disaster literacy than the poorer southern districts; specialised disaster training programmes can be effective, especially if targeted at low-income households.
Efforts to build trust between citizens and the organisations responsible for disaster management, along with educating people about the potential risks and frequency of disasters in the region, can help motivate them to be better prepared.
Iran is a disaster-prone country that has experienced more than 250 natural disasters over the past century, including floods, earthquakes, droughts and storms. These disasters have affected more than 60 million people, killed at least 158,350, and caused an estimated damage of more than US$53 billion (EM-DAT 2021). Several recent studies have addressed the socio-economic effects of various types of natural disasters and climate change in Iran (Farzanegan, Feizi, and Gholipour 2021; Farzanegan, Gholipour, and Javadian 2023; Farzanegan and Fischer 2023; Fischer 2021).
In a recent study (Farzanegan et al 2024), we provide new empirical evidence on the individual characteristics that shape disaster preparedness and disaster literacy in Iran. The analysis adds new insights to previous studies on disaster literacy, which, apart from two recent case studies from Turkey (Genc et al. 2022; Türker and Sözcü 2021), mainly focus on regions other than the Middle East and North Africa.
Disaster literacy, closely related to concepts such as disaster experience, risk perception, and disaster preparedness, can be defined as “an individual’s capacity to read, understand, and use information to make informed decisions and follow instructions in the context of mitigating, preparing, responding, and recovering from a disaster” (Brown, Haun, and Peterson 2014). Brown et al (2014) developed a model with four stages of disaster literacy that we use in our study: basic disaster literacy, functional disaster literacy, interactive disaster literacy, and critical disaster literacy.
Several previous studies have addressed the topic of disaster literacy using different definitions and approaches and focusing on different countries, such as Taiwan (Chung and Yen 2016), China (Zhang et al. 2021), Nigeria (Daramola, Odunsi, and Olowoporoku 2018) and Turkey (Genc et al. 2022). These studies highlight the importance of school curricula that equip students with disaster recognition knowledge. These empirical studies reveal that socio-economic characteristics such as age, field of study, grade, place of residence, educational level of parents, and employment positively affect disaster literacy. Additionally, the experience of natural disasters, previous disaster training, and preparation within the family also enhance disaster literacy. However, these studies commonly find that participants typically have, at best, mediocre levels of disaster literacy.
Research question, data and methodology
The research question of our study is: What are the main determinants of disaster literacy within the population of Tehran? After identifying these determinants, we create a Disaster Literacy Index (DLI) with four stages.
To answer this question, we analyzed survey data from 502 respondents in Tehran, collected in December and January 2021. The representative survey was conducted by IranPoll and financially supported by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), Bourse & Bazaar Foundation, Institute of International Education (IIE), and the IranPoll Opinion Research Support Fund.
Our objective is to understand how disaster literacy is associated with previous experience with natural disasters, emotions towards natural disasters, level of education, household income, and institutional trust. This leads to the following five hypotheses:
- Hypothesis 1: Having experienced natural disasters is associated with a higher probability of being disaster literate.
- Hypothesis 2: Fearing natural disasters is associated with a higher probability of being disaster literate.
- Hypothesis 3: A higher level of education is associated with a higher probability of being disaster literate.
- Hypothesis 4: Being from a wealthier household is associated with a higher probability of being disaster literate.
- Hypothesis 5: Trusting Iran’s natural disaster management is associated with a higher probability of being disaster literate.
Findings
The results of the empirical investigation suggest that household income level, trust in Iran’s natural disaster management, fear of natural disasters, perceived frequency of natural disasters, and internet usage are all positively associated with natural disaster literacy.
Additionally, we created a Disaster Literacy Index (DLI) for Tehran, ranging from 0 to 100, using 14 natural disaster literacy indicators. This index ranges from 0, indicating no disaster literacy, to 100, representing the highest possible disaster literacy. The aim is to capture the four stages of disaster literacy discussed by Brown et al (2014).
Regarding the hypotheses, the results indicate that fear (Hypothesis 2), income (Hypothesis 4), and trust (Hypothesis 5) are positively associated with DLI scores, while experience (Hypothesis 1) and education (Hypothesis 3) do not show statistically significant results at conventional levels. For instance, respondents who trust Iran’s disaster management have, on average, a DLI score 5.5 points higher than the average respondent in the sample, and those who reported a high income have, on average, a DLI score 5.0 points higher.
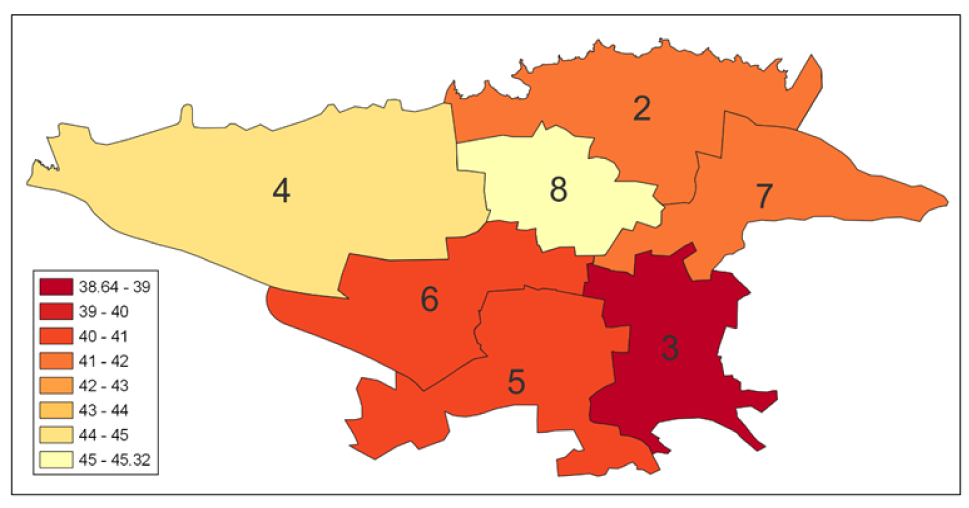
When comparing the average DLI scores of the northern and southern districts, spatial inequality within Tehran becomes evident. The northern subsample has significantly higher DLI scores than the southern subsample (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Average DLI in Tehran’s phone districts
Conclusion
The research findings highlight the limited impact of natural disaster experience and formal education on natural disaster literacy, emphasizing the effectiveness of specialized disaster training programs, especially those targeted at low-income households.
Moreover, efforts to build trust between citizens and the organizations responsible for natural disaster management, along with educating people about the potential risks and frequency of natural disasters in the region, can help motivate them to be better prepared.
Further reading
Brown, Lisa M., Jolie N. Haun, and Lindsay Peterson. 2014. “A Proposed Disaster Literacy Model.” Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness 8 (3): 267–75. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2014.43.
Chung, Sung-Chin, and Cherng-Jyh Yen. 2016. “Disaster Prevention Literacy among School Administrators and Teachers: A Study on the Plan for Disaster Prevention and Campus Network Deployment and Experiment in Taiwan.” Journal of Life Sciences 10:203–14. https://doi.org/10.17265/1934-7391/2016.04.006.
Daramola, Oluwole, Oluwafemi Odunsi, and Oluwaseun Olowoporoku. 2018. “The Corridor to Survival: Assessment of Disaster Management Literacy in a Developing Country.” Environmental Quality Management 27 (2): 15–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.21525.
EM-DAT. 2021. “The International Disaster Database, Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED), Université Catholique de Louvain.” 2021. https://public.emdat.be.
Farzanegan, Mohammad Reza, Mehdi Feizi, and Hassan F. Gholipour. 2021. “Drought and Property Prices: Empirical Evidence from Provinces of Iran.” Economics of Disasters and Climate Change 5:203–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41885-020-00081-0.
Farzanegan, Mohammad Reza, and Sven Fischer. 2023. “The Impact of a Large-Scale Natural Disaster on Local Economic Activity: Evidence from the 2003 Bam Earthquake in Iran.” CESifo Working Paper No. 10502 (June). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4477990.
Farzanegan, Mohammad Reza, Sven Fischer, and Peter Noack. 2024. “Natural Disaster Literacy in Iran: Survey-Based Evidence from Tehran.” International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 100 (January):104204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.104204.
Farzanegan, Mohammad Reza, Hassan F. Gholipour, and Mostafa Javadian. 2023. “Air Pollution and Internal Migration: Evidence from an Iranian Household Survey.” Empirical Economics 64:223–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-022-02253-1.
Fischer, Sven. 2021. “Post-Disaster Spillovers: Evidence from Iranian Provinces.” Journal of Risk and Financial Management 14(5) (193). https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14050193.
Genc, Fatma Zehra, Suzan Yildiz, Emine Kaya, and Naile Bilgili. 2022. “Disaster Literacy Levels of Individuals Aged 18–60 Years and Factors Affecting These Levels: A Web-Based Cross-Sectional Study.” International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 76 (June):102991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.102991.
Türker, Abdullah, and Ufuk Sözcü. 2021. “Examining Natural Disaster Literacy Levels of Pre-Service Geography Teachers.” Journal of Pedagogical Research 5 (2): 207–21. https://doi.org/10.33902/JPR.2021270164.
Zhang, Di, Xiaofang Zhu, Zhengrong Zhou, Xiao Xu, Xueying Ji, and Aihua Gong. 2021. “Research on Disaster Literacy and Affecting Factors of College Students in Central China.” Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness 15 (2): 216–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2020.33.




