In a nutshell
Renewable energy projects promise great economic benefits in terms of driving green growth and achieving sustainable development; they are of paramount importance for reducing harmful gas emissions, especially through diversifying economies and investing in energy efficiency.
To consolidate security and political stability in the region, governments of GCC countries need to manage their political and economic systems amid the global transition away from carbon-based economies.
The success of the transition will depend on governments’ capacity to deliver economic diversification, investment in sustainable infrastructure, and the development of renewable energy to enhance resilience and adapt to climate-related risks.
All the countries in the GCC region have announced goals for raising the share of renewable energy in their energy mix. Bahrain recently doubled its targets to achieve 20% of its total energy mix by 2035; Kuwait has announced a target of 15% by 2030; Oman has announced a target of 10% by 2025 and 30% by 2030; and Qatar has announced a target of 20% by 2030. Saudi Arabia has set the most powerful target in the Gulf, with a goal of generating 50% renewable energy for electricity by 2030, followed by the United Arab Emirates (UAE), which has set a clean energy target of 44% by 2050.
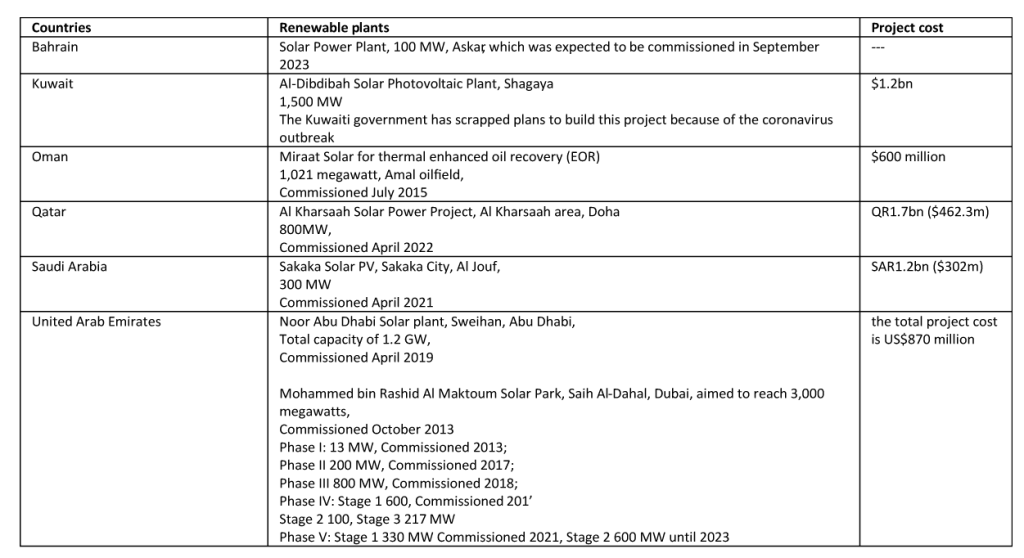
The GCC countries have started the energy transition and they are continuing the implementation process through large-scale renewable projects (see Table 1). Each country has its own unique initiatives and goals to shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
Table 1: The largest energy megaprojects in the GCC countries
Green opportunities
The GCC region presents significant opportunities for investing in the energy transition. Indeed, the region is endowed with abundant renewable energy resources, particularly solar and wind energy (Basha et al, 2021). The use of these resources can help to achieve lower reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, investing in renewable energy can create job opportunities, enhance energy security, and improve air quality (Alnaser et al, 2022). The GCC countries can also leverage sustainable energy to drive green growth and achieve sustainable development by diversifying their economies. It will be possible to create new jobs, reduce energy costs, improve air quality and attract foreign investment by investing in renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable transport and the circular economy, as well as through international cooperation.
Key challenges
Among the main challenges is the current dominance of fossil fuels in the energy mix, which has led to a lack of incentives and policies to promote renewable energy. The presence of high hydrocarbon subsidies and a low electricity tariff structure also discourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies (Al-Sarihi and Mansouri, 2022).
The shift to alternative revenue sources requires careful social and economic preparation. Novertheless, the harsh climatic conditions in the GCC region stand as an obstacle to the efficient operation and maintenance of renewable energy facilities, and they complicate the process. The lack of infrastructure combined with the high upfront cost of investment can also pose additional challenges to the energy transition in the region.
The GCC and the geopolitics of the energy transition
The Gulf region is at the core of the global waves of energy and climate change-related geopolitical development. Political tensions and geopolitical rivalries within the region hinder the development of a cooperative approach to mitigate the effects of climate change and impede integrated regional collaborations (Beni et al, 2021).
To consolidate their security and political stability in the region, the GCC countries should balance their relations with the regional powers, respond to the fallout of regional and global crises, and manage their political and economic systems amid the global shift away from carbon-based energy sources. The Gulf states will try to stay in a good position internationally as oil and gas are managed outside the global economy through multilateral climate diplomacy (Strategic Comments, 2022).
The Gulf states and the post-oil era
The Gulf states recognise the importance of preparing for the post-carbon era, and seeking to diversify their economies and achieve sustainability. The success of this transition will depend on the countries’ capability of fulfilling various conditions, including diversifying their economies, ecologically modernising Gulf societies, reducing environmental risks, enhancing GCC-wide cooperation (Al-Saidi, 2020) and promoting research in renewable energy.
The success of the transition will also depend on the capacity of the GCC countries to mitigate environmental risks. Indeed, governments should use a range of economic tools that can play a crucial role in promoting climate change mitigation and adaptation in the region, including subsidy reform, green bonds, energy efficiency standards and carbon taxes (Miniaoui, 2023).
Further reading
Alnaser, NW, HM Albuflasa and WE Alnaser (2022) ‘The Transition in Solar and Wind Energy Use in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries (GCCC)’, Renewable Energy and Environmental Sustainability 7: 4.Al-Saidi, M (2020) ‘From Economic to Extrinsic Values of Sustainable Energy: Prestige, Neo-Rentierism, and Geopolitics of the Energy Transition in the Arabian Peninsula’, Energies 13(21): 5545.
Al-Sarihi, A, and N Mansouri (2022) Renewable Energy Development in the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries: Status, Barriers, and Policy Options’, Energies 5(15): 1923.
Basha, J, T Jafary, R Vasudevan, J Bahadur, MA Ajmi et al (2021) ‘Potential of Utilization of Renewable Energy Technologies in Gulf Countries’, Sustainability 13(18): 10261.
Beni, AN, N Marriner, A Sharifi, J Azizpour, K Kabiri, M Djamali and A Kirman (2021) ‘Climate Change: A Driver Of Future Conflicts in the Persian Gulf Region?’, Heliyon 2(7): e06288.
Miniaoui, H (2023) ‘Climate Change in the Middle East and North Africa: Between the repercussions of a lived reality and opportunities for a brighter future’, ERF Policy Brief No. 109.
Strategic Comments (2022) ‘The Arab Gulf states and the geopolitics of the energy transition’, Strategic Comments28:2.


